A Comprehensive Guide on Service Management
In today’s fast-paced and customer-centric business environment, organizations must ensure that their services meet customer expectations while staying competitive.
Enter service management – the systematic approach to planning, designing, delivering, and continuously improving services within an organization.
This methodology is integral to maintaining customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and long-term business success. But what exactly is service management, and why does it matter? Let’s dive in.
Defining Service Management
Service management encompasses the processes, tools, and strategies an organization employs to ensure that its services align with customer needs and expectations. It goes beyond simply delivering services; it focuses on optimizing every aspect of the service lifecycle, from conception to continuous improvement.
Typically working hand in hand with service design methodologies, service management aims to:
- Provide seamless service delivery.
- Maximize customer satisfaction.
- Enhance service quality through ongoing refinement.
In essence, service management is about creating value – for customers and the organization itself.
The Core Components of Service Management
The methodology revolves around four key activities: planning, design, delivery, and improvement. Each phase plays a crucial role in ensuring the overall success of the services offered.
1. Service Planning
Service planning lays the foundation for successful service delivery. During this phase, organizations develop detailed plans that outline:
- The scope of services: What services will be offered?
- Target audience: Who are the customers?
- Delivery strategy: What steps are needed to provide these services effectively?
A well-structured service plan aligns business objectives with customer needs, ensuring clarity and purpose from the outset.
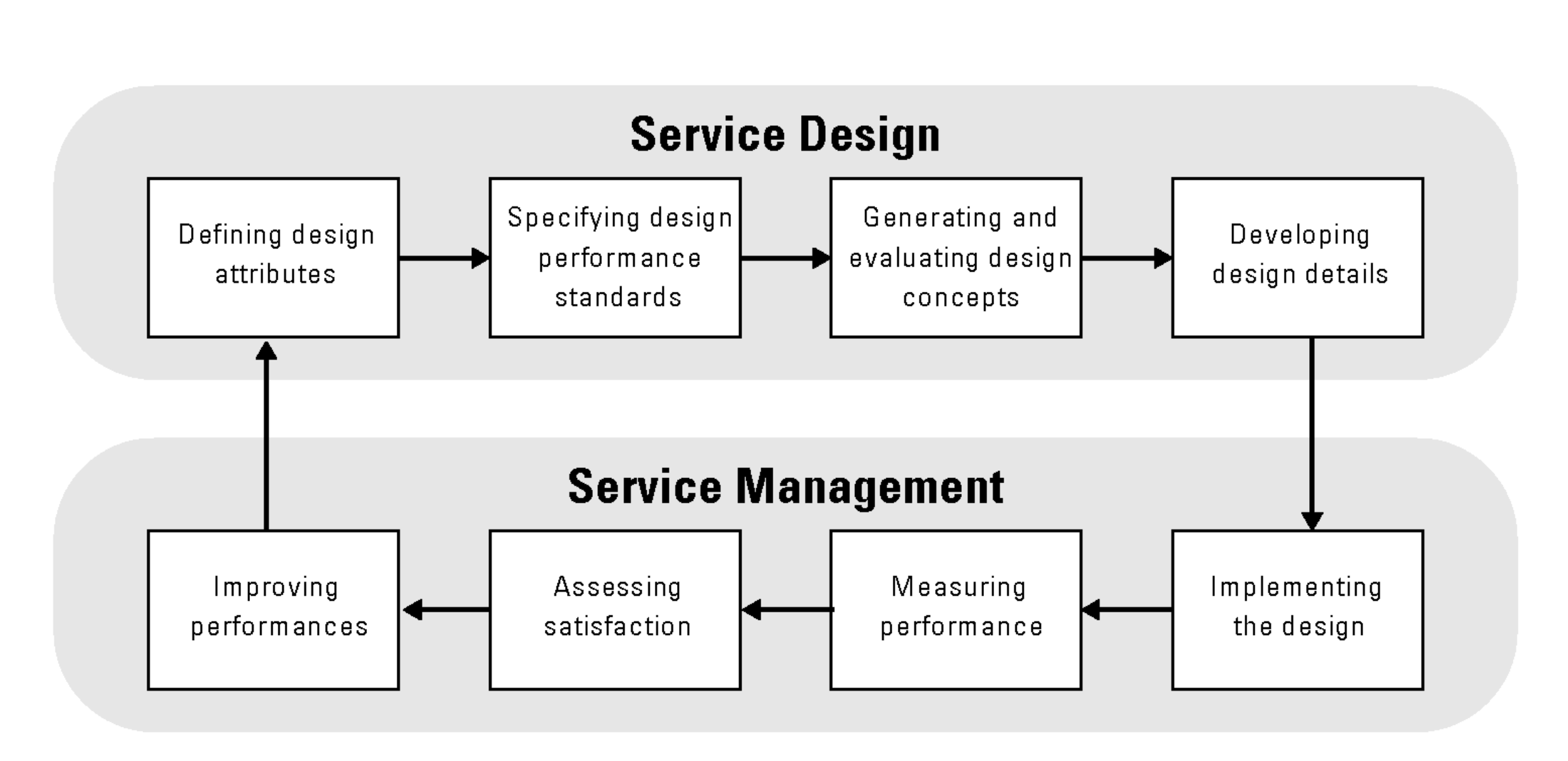
2. Service Design
The design phase is where the concept becomes tangible. This stage involves:
- Defining the features, functions, and performance requirements of the service.
- Crafting the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) to ensure accessibility and satisfaction.
- Establishing clear performance metrics to measure success.
Service design is a critical step that determines how customers interact with and perceive the service.
3. Service Delivery
This phase focuses on executing the service as planned and designed. Key elements include:
- Infrastructure deployment: Setting up the technical and operational framework.
- Training and onboarding: Ensuring that employees and users understand how to use the service effectively.
- Ongoing support: Providing maintenance, troubleshooting, and updates to maintain service quality.
4. Service Improvement
Continuous improvement is the hallmark of effective service management. This stage involves:
- Evaluating performance: Using metrics and customer feedback to identify strengths and weaknesses.
- Implementing changes: Addressing gaps and enhancing the service.
- Monitoring outcomes: Ensuring that improvements deliver tangible value.
Tools and Techniques in Service Management
To achieve its objectives, service management relies on a variety of tools and techniques:
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Formal agreements that define the expected level of service.
- Performance Metrics: Key performance indicators (KPIs) and benchmarks to track progress.
- Customer Feedback Mechanisms: Surveys, reviews, and direct feedback to understand user satisfaction.
- Service Catalogs: Comprehensive documentation of all available services, their features, and benefits.
These tools help organizations maintain transparency, accountability, and a customer-first approach.
Why Service Management Matters
The methodology isn’t just a back-office function; it’s a strategic imperative. Here’s why:
1. Customer Satisfaction
In a highly competitive marketplace, delivering services that meet or exceed customer expectations can be a significant differentiator. Effective service management ensures that customer needs are prioritized, resulting in higher satisfaction and loyalty.
2. Operational Efficiency
By streamlining processes and minimizing waste, service management helps organizations deliver value while optimizing resource utilization. This can lead to cost savings and improved profitability.
3. Continuous Improvement
The methodology fosters a culture of ongoing refinement, enabling organizations to adapt to changing market demands and technological advancements.
4. Enhanced Collaboration
With its structured approach, service management encourages cross-functional collaboration, breaking down silos and ensuring cohesive teamwork.
Best Practices for Effective Service Management
To excel in service management, organizations should adhere to the following best practices:
- Adopt a Customer-Centric Mindset: Always design and deliver services with the end user in mind.
- Leverage Technology: Use modern tools like IT service management (ITSM) platforms to automate and streamline processes.
- Focus on Data: Collect and analyze performance data to make informed decisions.
- Empower Employees: Provide training and resources to ensure teams can deliver exceptional service.
- Foster Feedback Loops: Actively seek and act on customer and employee feedback to drive improvements.
Real-World Applications of Service Management
The methodology principles are applied across various industries and domains, including:
- IT Services: Managing IT infrastructure, software, and support services (e.g., ITIL framework).
- Healthcare: Streamlining patient care services and medical resource management.
- Retail: Enhancing customer experiences through efficient supply chain and inventory management.
- Hospitality: Delivering consistent and high-quality guest services.
Each application underscores the versatility and value of service management.
Key Frameworks and Standards
Several established frameworks guide service management practices, including:
- ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library): Widely used in IT service management to standardize and optimize processes.
- ISO 20000: An international standard for service management systems.
- COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies): Focuses on IT governance and management.
- Lean and Six Sigma: Techniques for improving efficiency and quality in service delivery.
Future Trends in Service Management
As technology and customer expectations evolve, service management is poised for significant transformation. Key trends include:
- AI and Automation: Leveraging AI-powered tools to enhance efficiency and personalization.
- Self-Service Portals: Empowering customers to resolve issues independently.
- Sustainability: Incorporating eco-friendly practices into service delivery.
- Personalization: Tailoring services to meet individual customer preferences.
Conclusion
Service management is a cornerstone of modern business operations. By systematically planning, designing, delivering, and improving services, organizations can drive customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and long-term success.
Whether you’re a small business or a global enterprise, adopting robust service management practices is essential for thriving in today’s dynamic marketplace.
For more insights on service management and best practices, explore resources like:
By embracing service management, you can transform the way your organization delivers value and stays ahead of the curve.
If you’re interested in continuous learning about how to Design products/services please check out Nicola Morelli’s paper about that.