A Comprehensive Guide to UX (User Experience)
Introduction
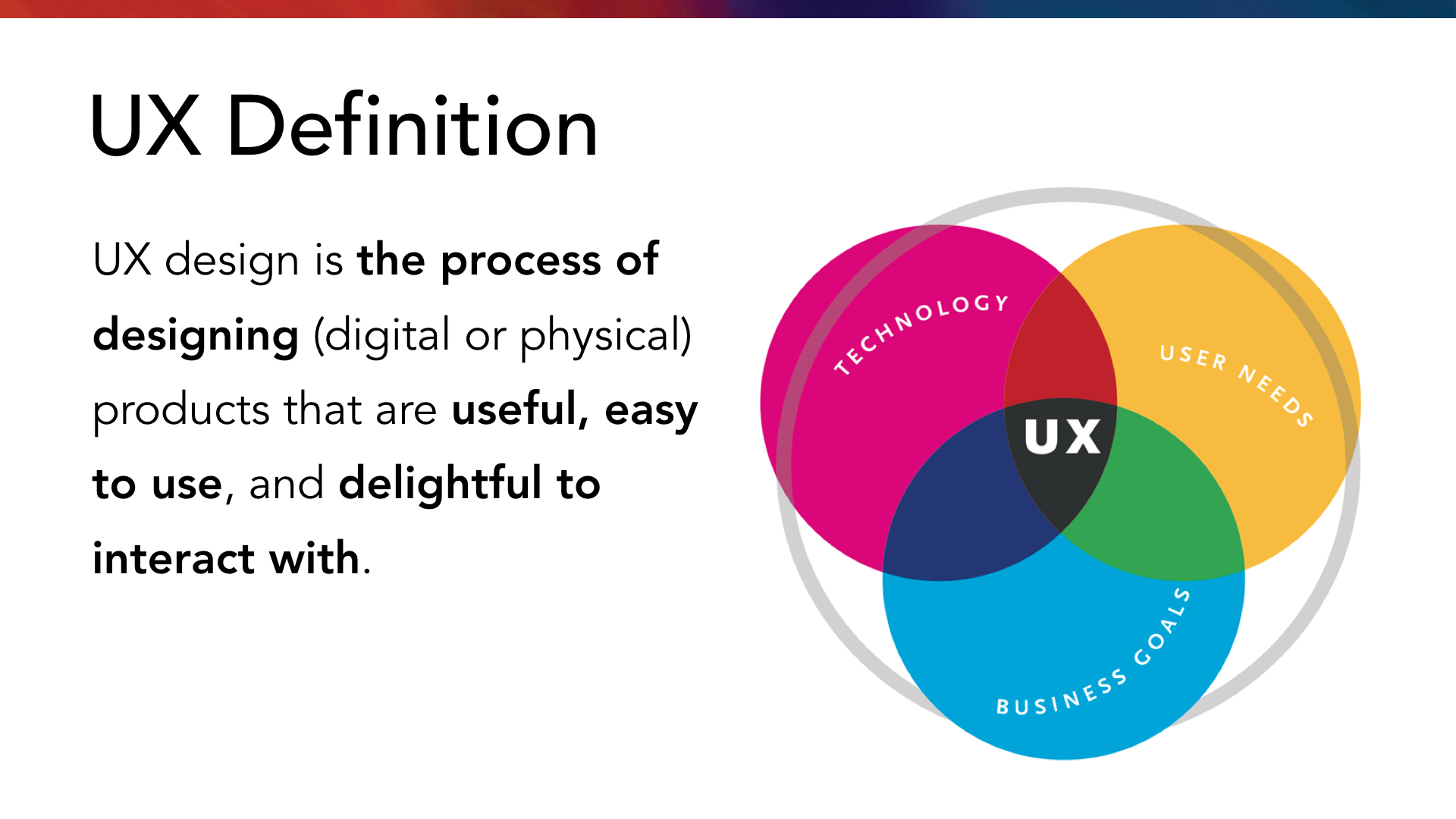
UX is the overall interaction and satisfaction a person derives from using a product, system, or service. User Experience design focuses on crafting seamless, efficient, and enjoyable experiences for users, emphasizing usability, accessibility, and emotional resonance. In an age driven by technology, understanding and prioritizing UX has become a cornerstone for businesses aiming to stay competitive and relevant.
Origins of UX
The term “User Experience” was first introduced by Don Norman, a cognitive scientist and usability expert, in the early 1990s. At the time, Norman recognized the need for a design approach that went beyond functionality and usability, encapsulating the entire journey and interaction a user has with a product. His insights laid the foundation for modern UX design, integrating principles of psychology, design, and technology to create holistic user-centered solutions.
Core Principles of UX Design
At its heart, UX design aims to solve real-world problems by understanding users’ needs, behaviors, and pain points. Several guiding principles shape this discipline:
- Usability Usability ensures that a product or service is intuitive and straightforward. An easy-to-navigate interface, clear instructions, and logical workflows are all hallmarks of good usability. For instance, websites like Amazon prioritize simple navigation to help users quickly find and purchase products.
- Accessibility Accessibility ensures that products are usable by individuals with diverse abilities. This includes designing for screen readers, incorporating keyboard navigation, and ensuring color contrast meets accessibility standards. Platforms like Apple’s iOS exemplify accessibility with features like VoiceOver and AssistiveTouch.
- Emotional Design Emotional design considers how users feel while interacting with a product. The aesthetics, tone of voice, and micro-interactions play a significant role in creating positive emotional experiences. Instagram’s seamless interface and engaging animations are examples of emotional design that fosters user delight.
- Feedback Providing users with timely and relevant feedback ensures clarity and reduces uncertainty. Whether it’s a confirmation message for a successful transaction or an error notification, feedback is crucial for guiding users.
- Efficiency Efficiency minimizes the effort required to complete tasks. For example, Google’s autocomplete feature in its search engine significantly reduces the time users spend typing.
- Learnability A well-designed product is easy for first-time users to understand while offering advanced features for experienced users. Products like Canva balance simplicity and depth, catering to novice and professional designers alike.
The UX Design Process
Creating exceptional User Experience involves a structured process that encompasses multiple stages:
1. Empathize
Designers start by understanding users’ needs, behaviors, and pain points through user research, interviews, and observations. Tools like empathy maps and user personas help in visualizing insights.
2. Define
Based on research findings, the next step is to define the problem statement clearly. This stage focuses on pinpointing the root cause of issues to ensure design efforts are targeted effectively.
3. Ideate
Brainstorming sessions are held to generate innovative solutions. Techniques like mind mapping and sketching are used to explore a wide range of ideas before narrowing them down.
4. Prototype
Designers create prototypes—tangible representations of ideas—to visualize and test concepts. Prototypes can range from low-fidelity wireframes to high-fidelity interactive models.
5. Test
Usability testing involves evaluating prototypes with real users to gather feedback. Iterative improvements are made based on findings to ensure the design meets user expectations.
Applications of UX Design
UX design is not limited to digital products but spans various domains, including:
- Product Design: Physical products like smartphones and wearable devices rely on UX principles to ensure functionality and desirability.
- Service Design: Designing customer journeys for services like healthcare, banking, and hospitality to ensure seamless interactions.
- Digital Experiences: Websites, mobile apps, and software applications are primary beneficiaries of UX design.
- Social Innovation: Using UX to address societal challenges, such as designing tools for education or healthcare in underserved communities.
Importance of UX in Modern Businesses
- Enhanced User Satisfaction Good UX design leads to satisfied users who are more likely to return, recommend, and engage with a product.
- Increased Conversion Rates UX optimizations, like simplifying checkout processes or improving navigation, can significantly boost conversions. Shopify’s user-friendly interface is a testament to this.
- Cost Savings Addressing usability issues early in the design process reduces the cost of fixing problems post-launch. According to the Nielsen Norman Group, fixing a usability problem during development costs ten times less than after launch.
- Competitive Advantage Companies that prioritize UX stand out in crowded markets. For instance, Airbnb revolutionized the travel industry by focusing on user needs and creating a seamless booking experience.
Challenges in UX Design
Despite its benefits, UX design comes with challenges:
- Balancing business goals with user needs.
- Designing for diverse audiences with varying preferences and abilities.
- Keeping pace with rapidly evolving technology and user expectations.
- Gathering actionable insights from user research.
The Future of UX Design
As technology evolves, UX design continues to adapt. Key trends shaping the future of UX include:
- AI and Machine Learning Personalized user experiences powered by AI are becoming more common. Netflix’s recommendation engine is a prime example of AI-driven UX.
- Voice and Conversational Interfaces With the rise of smart assistants like Alexa and Siri, designing for voice interactions is becoming essential.
- Sustainability Designers are increasingly focusing on creating eco-friendly digital experiences by reducing data usage and energy consumption.
- Immersive Experiences Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are opening new frontiers in UX, enabling more interactive and engaging user experiences.
Conclusion
UX design is integral to creating products and services that resonate with users, addressing their needs, and exceeding their expectations. By combining usability, accessibility, and emotional design, UX practitioners craft experiences that drive engagement, loyalty, and success.
Investing in UX is not just a design decision but a strategic move that can transform businesses, elevate user satisfaction, and pave the way for innovation.