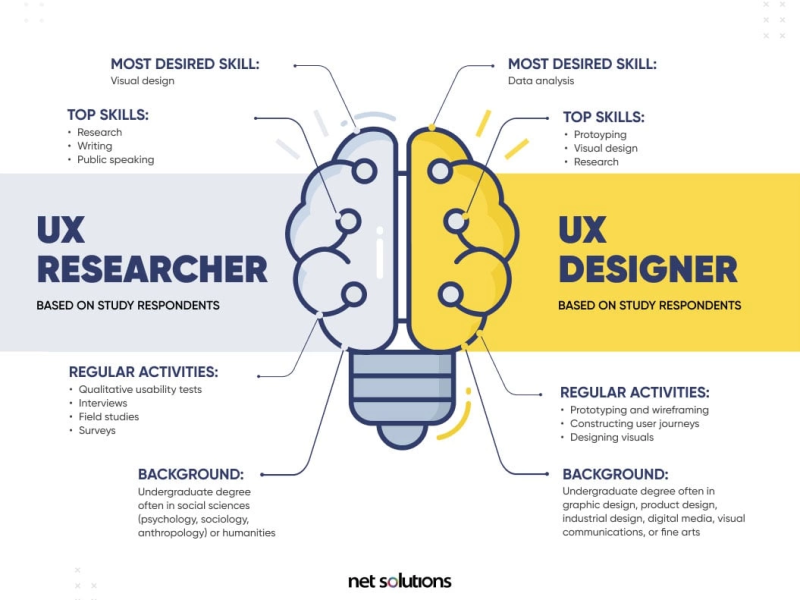
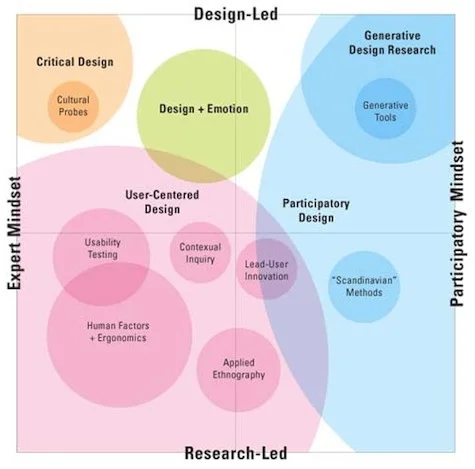
In the previous post, we explored the foundational principles of User Experience (UX) design—a discipline focused on creating intuitive and engaging digital experiences.
Building on that discussion, this post dives into the next level of UX design best practices, offering actionable insights for continuously refining designs, ensuring accessibility, optimizing for diverse devices, crafting visually appealing interfaces, and providing clear user guidance.
These practices are essential for creating user-centered products that resonate with diverse audiences.
Continuously Iterating and Improving Designs Based on User Feedback
Iteration is at the heart of UX design, enabling designers to refine and optimize interfaces by incorporating user feedback. This ongoing process ensures alignment with user needs and expectations, leading to higher satisfaction and engagement.
Best Practices for Continuous Iteration:
- Prioritize Feedback: Analyze user feedback to identify the most impactful issues. Focus on solving problems that significantly affect the user experience.
- Tools: Use platforms like Hotjar or Google Forms to gather user insights.
- Test and Validate: Prototype solutions and test them with real users before implementing changes.
- Resources: Learn more about usability testing at Nielsen Norman Group.
- Track Progress: Maintain a changelog to document improvements and assess the impact of design iterations.
- Involve Users Early: Engage users during the design process to co-create solutions.
- Monitor Metrics: Use analytics tools like Google Analytics or Mixpanel to track KPIs such as user engagement and task success rates.
- Stay Agile: Embrace a continuous improvement mindset to adapt to evolving user needs and technological advancements.
Why It Matters: Iteration drives innovation and usability. By validating changes with user feedback, designers build products that resonate with audiences, fostering loyalty and trust.
Ensuring Accessibility for Users with Disabilities
Accessibility in UX design ensures inclusivity, making digital products usable by people with diverse abilities. Adhering to standards like the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) promotes equitable access.
Best Practices for Accessibility:
- Follow Standards: Align with WCAG and ADA guidelines.
- Learn more at W3C Web Accessibility Initiative.
- Provide Alternatives: Offer keyboard navigation, voice commands, and adjustable font sizes.
- Use Simple Language: Design with clear and understandable text to accommodate users with cognitive impairments.
- Offer Text Alternatives: Use descriptive alt text for images and captions for videos.
- Test with Real Users: Collaborate with users who have disabilities to identify pain points.
- Continuously Update: Stay informed about evolving accessibility standards.
Why It Matters: Accessible designs foster inclusivity, enhancing usability for all users and complying with legal standards, ultimately expanding a product’s reach.
Optimizing for Various Device Sizes and Screen Resolutions
Responsive design ensures seamless experiences across devices—a critical need in an era where users switch between smartphones, tablets, and desktops.
Best Practices for Responsive Design:
- Adopt Fluid Grids: Design layouts that adapt to different screen sizes.
- Tools: Frameworks like Bootstrap or Tailwind CSS facilitate responsive designs.
- Use Flexible Images: Ensure visuals scale proportionally without losing quality.
- Test Across Devices: Regularly test designs on various devices and resolutions.
- Tools: Use BrowserStack or Responsinator for testing.
- Prioritize Touch Interactions: Optimize for gestures like tapping and swiping on touch screens.
- Maintain Text Legibility: Ensure sufficient font size and contrast ratios.
- Support Orientation Changes: Design for both portrait and landscape modes.
- Monitor Performance: Continuously refine designs to meet evolving device capabilities.
Why It Matters: Optimizing for diverse devices enhances user satisfaction and accessibility, reducing bounce rates and increasing engagement.
Creating Visually Appealing and Intuitive Designs
Aesthetics and usability go hand in hand in UX design. Striking the right balance between visual appeal and functionality fosters positive first impressions and long-term engagement.
Best Practices for Intuitive Design:
- Embrace Simplicity: Use minimalistic designs with clear navigation.
- Ensure Consistency: Maintain a cohesive design system.
- Inspiration: Explore Google’s Material Design for ideas.
- Focus on User Goals: Align design elements with user priorities.
- Leverage Visual Hierarchy: Use size, contrast, and placement to guide attention.
- Incorporate Storytelling: Use visuals to communicate narratives.
- Use Motion Design: Add animations to enhance usability without overwhelming users.
- Test Regularly: Validate design choices through usability testing.
Why It Matters: A visually appealing interface enhances user trust and satisfaction while intuitive navigation ensures task completion and reduces frustration.
Providing Clear and Concise Guidance and Feedback
Effective guidance and feedback empower users to navigate interfaces effortlessly and recover from errors seamlessly.
Best Practices for User Guidance:
- Use Clear Microcopy: Craft intuitive labels, buttons, and error messages.
- Resource: Learn more about microcopy at UX Writing Hub.
- Incorporate Visual Cues: Use icons, colors, and tooltips for context.
- Employ Progressive Disclosure: Reveal information incrementally to avoid overwhelming users.
- Offer In-Context Help: Embed support directly into tasks.
- Prevent Errors: Design workflows that minimize the likelihood of mistakes.
- Enable Error Recovery: Provide clear instructions for troubleshooting and recovery.
Why It Matters: Guidance and feedback improve user confidence, streamline task completion, and foster a sense of control, ultimately enhancing the overall experience.
Common UX Design Mistakes to Avoid
Even seasoned designers can make missteps. Awareness of common pitfalls can prevent costly errors.
- Skipping User Research: Designs uninformed by research risk misalignment with user needs.
- Learn more about user research at Usability.gov.
- Ignoring Accessibility: Overlooking inclusivity limits the audience and can lead to compliance issues.
- Information Overload: Simplify interfaces to avoid overwhelming users.
- Disregarding Feedback: Incorporate user insights to address pain points effectively.
- Neglecting Testing: Validate designs to uncover usability issues before launch.
Conclusion
Adhering to UX design best practices ensures the creation of intuitive, inclusive, and visually compelling digital experiences. By embracing continuous iteration, prioritizing accessibility, optimizing for diverse devices, crafting intuitive designs, and providing clear guidance, designers can deliver products that delight users and drive engagement.
Stay tuned for the next installment in our series, where we’ll delve deeper into advanced UX methodologies and tools. Meanwhile, explore resources like NNG, WCAG, and Material Design to enhance your UX knowledge.
If you want to continue learning about this topic, you should visit the below links: