Digital Transformation A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Its Impact on Businesses
In the ever-evolving world of business, digital transformation has become a buzzword that is shaping the future of organizations worldwide.
It’s more than just upgrading technology; it’s a fundamental change in how companies operate and deliver value to their customers.
From artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud computing to the Internet of Things (IoT), digital transformation encompasses a wide range of technologies that can drastically improve efficiency, reduce costs, and drive innovation.
In this blog post, we will explore the definition, pillars, stages, best practices, and common mistakes related to digital transformation, all aimed at providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this essential business process.
Read more about the importance of digital transformation.
What is Digital Transformation?
Digital transformation refers to the process of adopting and implementing digital technologies to fundamentally change how a company operates and delivers value to its customers. This shift is not just about the technology itself but also involves a change in business models, operational strategies, and the company’s culture. The aim is to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and increase competitiveness.
For more insights on how digital transformation is reshaping industries, visit Forbes.
The Core Technologies Behind Digital Transformation
Some of the key technologies driving digital transformation include:
- Cloud Computing: By moving data and processes to the cloud, companies can eliminate the need for costly on-premises infrastructure. Cloud services offer flexibility, scalability, and cost savings.
Learn more about the benefits of cloud computing from Amazon Web Services.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI helps businesses automate routine tasks, improve decision-making, and gain insights from large datasets. For instance, AI can be used for customer service chatbots, predictive analytics, and machine learning-based recommendations.
For examples of AI in business, visit Harvard Business Review.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices allow businesses to collect real-time data from connected devices. This information can be used to improve operational efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and predict maintenance needs.
Explore IoT applications at IoT For All.
The Pillars of Digital Transformation
Successful digital transformation requires organizations to focus on several key elements, or pillars, that are critical to its success. These pillars guide the entire process, from strategy development to implementation. Below are the core pillars of digital transformation:
1. Leadership
Strong leadership is crucial for driving the process. Leaders must not only be visionary but also provide the resources and support necessary for the successful execution of the transformation process. Effective leadership involves promoting a culture of innovation and experimentation, encouraging teams to embrace change, and aligning transformation goals with the overall organizational strategy.
For more on the role of leadership in digital transformation, read McKinsey & Company’s insights.
2. Strategy
Having a well-defined strategy is essential for any organization. The strategy should outline specific goals, objectives, and actionable steps required to achieve success. It should also be aligned with the company’s overall business objectives and regularly updated to respond to changes in technology and the marketplace.
To dive deeper into creating an effective strategy, visit Gartner.
3. Culture
The transformation requires a shift in organizational culture. A culture that embraces change, innovation, and continuous learning is essential for successful transformation. Employees must feel empowered to adapt to new technologies and processes. Cultivating an inclusive and supportive environment helps encourage collaboration, experimentation, and risk-taking.
For more on cultivating a culture of innovation, check out Harvard Business Review on culture.
4. Technology
The backbone is the adoption of cutting-edge technologies. This includes not only infrastructure improvements (such as cloud computing and AI) but also customer-facing technologies that improve user experiences (e.g., mobile apps and customer portals). Businesses must carefully evaluate their technology stack to ensure it aligns with their long-term goals and provides a competitive advantage.
For up-to-date resources on digital technologies, explore Microsoft’s Digital Transformation.
5. Data
Data is at the heart of digital transformation. Collecting and analyzing data enables organizations to make informed decisions, improve operations, and deliver personalized customer experiences. A robust data management strategy is critical to ensuring that businesses can efficiently store, access, and analyze the massive volumes of data generated in the digital age.
To learn more about leveraging data, visit IBM’s Data Management Resources.
Best Practices
Implementing digital transformation successfully involves much more than simply deploying new technologies. Here are some best practices to guide organizations through the process:
1. Develop a Clear Strategy and Plan
A transformation initiative must begin with a comprehensive strategy and plan. The plan should outline the organization’s objectives, the technologies to be adopted, and the steps required to achieve the transformation. This strategy must be aligned with the overall business objectives and reviewed regularly to adjust for emerging trends and market changes.
Check out PwC’s Digital Transformation Guide for strategy development.
2. Involve All Stakeholders
The transformation affects every aspect of an organization, from employees to customers. It is crucial to involve all stakeholders, including key decision-makers, department heads, and even customers, in the transformation process.
Engaging stakeholders early on helps ensure that the transformation is seamless and meets the needs of everyone involved.
Read about how involving stakeholders leads to successful transformation at Digital Authority Partners.
3. Prioritize Customer Experience
The ultimate goal of the transformation process is to enhance the customer experience. By using technology to streamline processes, organizations can offer faster, more personalized services that meet the evolving expectations of customers. Listening to customer feedback, conducting research, and making customer-centric decisions will help ensure the transformation is successful.
For insights on improving customer experience with digital transformation, explore CX Network.
4. Embrace Data and Analytics
Organizations must harness the power of data to drive insights and decisions. By investing in data management platforms, businesses can analyze customer behavior, track performance metrics, and identify areas for improvement. Data-driven decision-making is crucial for optimizing operations and delivering value to customers.
Learn about the importance of data in digital transformation from Deloitte Insights.
5. Invest in Training and Development
The transformation requires employees to develop new skills and adapt to new technologies. Organizations should invest in training programs to ensure that employees are well-equipped to work with the latest tools and systems. Ongoing training is essential to keep employees up to date with the fast-paced nature of digital innovation.
Discover employee training strategies at LinkedIn Learning.
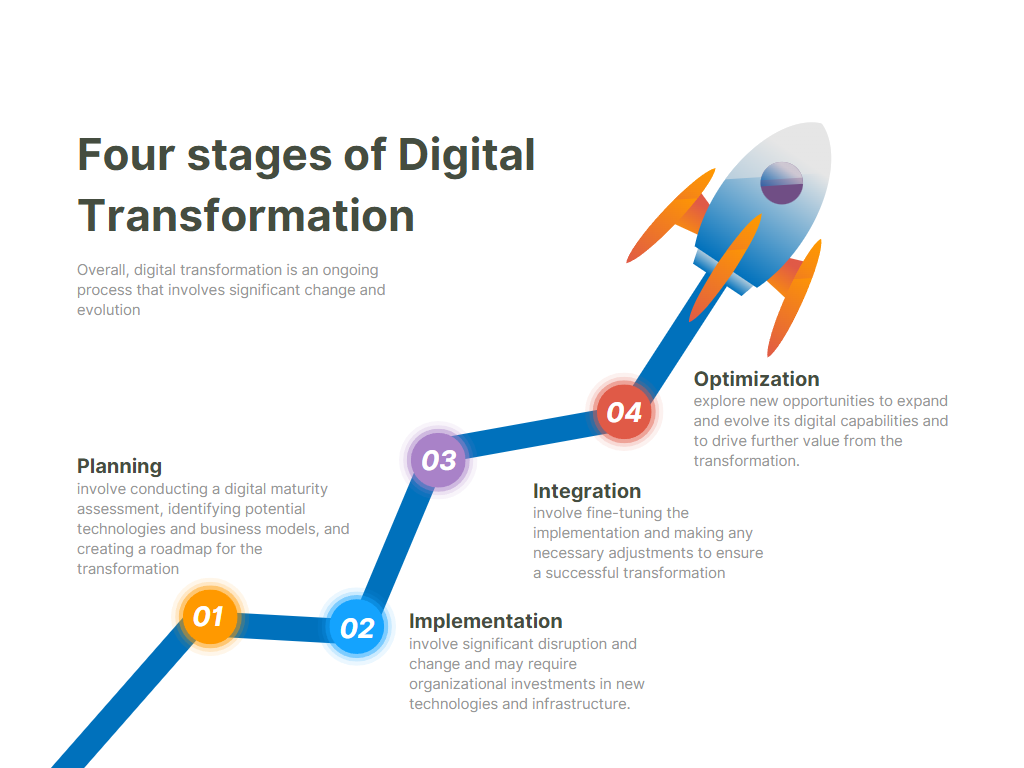
The Stages of Digital Transformation
Transformation is an ongoing process that typically unfolds in several stages. These stages help organizations break down the complex process into manageable steps:
1. Planning
The first stage of the transformation involves planning. During this phase, organizations assess their current digital maturity, identify areas for improvement, and set clear goals for the transformation. A digital maturity assessment is an essential tool during this stage, as it helps to understand where the organization stands in terms of technology adoption, processes, and culture.
Read more on digital maturity models at MIT Sloan Management Review.
2. Implementation
In the implementation stage, the organization starts adopting new technologies, updating processes, and training employees. This stage may involve significant disruptions, as new tools and systems are introduced. Companies must be prepared for this change, ensuring that they have the resources to support implementation.
Learn about successful implementation strategies at Gartner’s Transformation Tools.
3. Integration
Once new technologies are in place, organizations begin integrating them into their everyday operations. At this stage, the company starts to see the benefits of the transformation, such as improved efficiency and productivity. It’s essential to monitor progress and make adjustments where necessary.
For integration best practices, visit Capgemini’s Digital Transformation.
4. Optimization
The final stage of the transformation involves continuous optimization. In this phase, organizations refine their processes, analyze data to identify areas of improvement, and explore new opportunities for further innovation. This stage ensures that the company remains competitive and continues to evolve in the digital space.
Check out Accenture’s Digital Transformation Optimization.
Conclusion
Digital transformation is no longer optional but essential for organizations that wish to stay competitive in today’s fast-paced, technology-driven market. By understanding the core pillars, best practices, stages, and common mistakes, organizations can navigate the complexities of digital transformation and drive long-term success. As companies embrace these changes, they will enhance their customer experiences, optimize operations, and create new growth opportunities that will propel them forward in the digital age.
For more in-depth resources on digital transformation, visit McKinsey’s Digital Transformation.