A Comprehensive Guide on User Research
In today’s rapidly evolving digital world, understanding user needs is not just an advantage but a necessity.
Whether you’re building a new product or refining an existing one, user research is the cornerstone of creating solutions that resonate with real people.
But what exactly is user research, and how can it transform your design process? In this post, we’ll explore the core concepts, methods, tools, and stages of user research to help you harness its full potential.
What is User Research?
User research is the process of analyzing, studying, and understanding the needs, desires, challenges, behaviors, and motivations of the people who use a product or service.
It’s typically conducted to inform the design of new products or features or to improve an existing product. By uncovering how real users interact with a product, user research ensures that your designs are grounded in reality rather than assumptions.
The Importance of User Research
User research is critical because it helps to ensure that a product meets the needs and expectations of its users. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Informed Design Decisions: It provides actionable insights that guide design choices.
- Improved Usability: Understanding pain points allows for better user experiences.
- Increased Satisfaction: Products designed with user input tend to be more satisfying and efficient to use.
- Cost Savings: Identifying issues early in the design process reduces costly post-launch fixes.
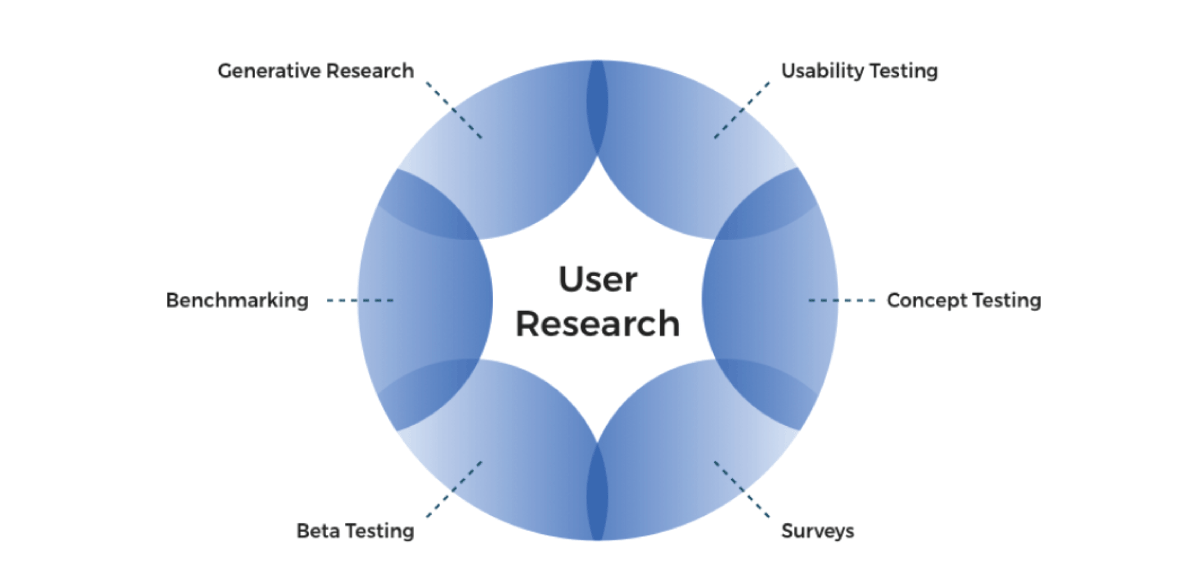
Types of User Research
The process can be broadly categorized into qualitative and quantitative methods:
1. Qualitative Research
Qualitative research focuses on understanding the “why” behind user behaviors. It involves methods like interviews and focus groups, offering in-depth insights into user motivations and challenges.
2. Quantitative Research
Quantitative research deals with numerical data and trends. Methods such as surveys and analytics help measure user behaviors and validate hypotheses.
When to Apply
User research is not a one-size-fits-all activity. It can be applied at various stages of the design process, depending on the project’s needs and goals:
1. Early in the Design Process
At the conceptual stage, the process helps define the product’s direction. Methods like user interviews and surveys can clarify user needs and expectations.
2. During the Design Process
Testing prototypes or early versions of a product can identify usability issues and refine designs.
3. Before Product Launch
Pre-launch testing ensures that the product is ready for release by addressing any final issues.
4. After Product Launch
Post-launch research gathers feedback to identify areas for improvement and ensure the product continues to meet user expectations.
Common Tools and Methods
A wide range of tools and methods can be used in user research. Here’s a breakdown of the most common ones:
1. Interviews
- Conducted in person, over the phone, or via video conferencing.
- Can be structured or unstructured.
- Often recorded and transcribed for analysis.
2. Focus Groups
- Small group discussions led by a moderator.
- Useful for gathering diverse perspectives.
- Can be conducted in person or online using collaboration tools.
3. Usability Testing
- Observing users as they interact with a product.
- Tools include screen recording software and eye-tracking devices.
4. Card Sorting
- Helps understand how users organize information.
- Participants group cards (representing items or concepts) into categories.
5. Surveys
- Can be conducted online or offline.
- Useful for gathering quantitative data on user preferences and behaviors.
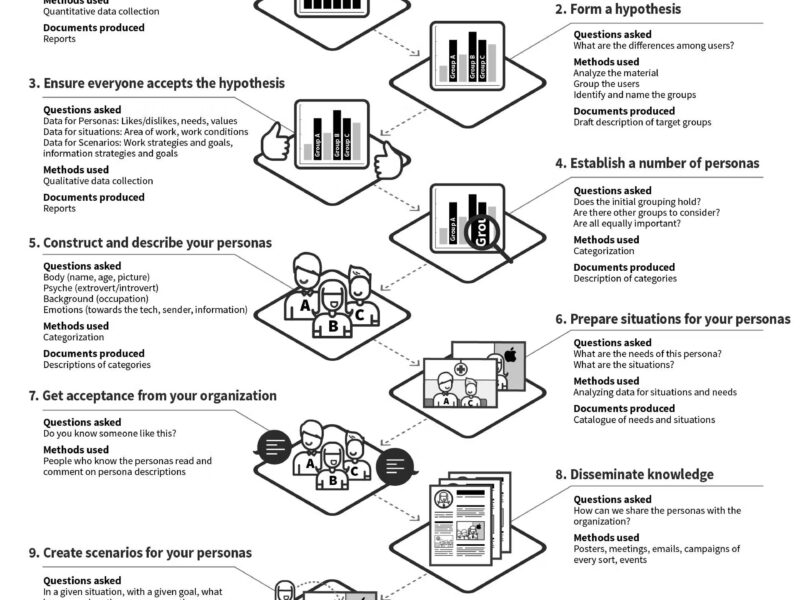
The User Research Process
Conducting user research involves several key steps:
1. Define Research Goals
Start by identifying specific questions or issues the research aims to address. Clear goals ensure focused and actionable outcomes.
2. Plan the Research
Choose the methods that align with your goals. Develop a research plan that outlines the steps, tools, and participant criteria.
3. Recruit Participants
Select participants who represent your target audience. Consider factors like demographics, behaviors, and needs.
4. Conduct the Research
Execute the planned methods, such as interviews, usability tests, or surveys. Ensure that data collection is systematic and unbiased.
5. Analyze the Data
Organize and interpret the collected data to uncover patterns, insights, and actionable recommendations.
6. Report the Findings
Summarize the research outcomes in a clear and concise report. Include key insights, supporting data, and design recommendations.
Real-World Examples of User Research
- Dropbox used user interviews to understand how professionals share files, leading to the development of features like shared folders and links.
- Spotify conducted usability testing to refine its app’s interface, ensuring an intuitive and enjoyable user experience.
- Google leverages surveys and analytics to continuously improve its search algorithms based on user feedback.
Best Practices for User Research
- Be Clear About Objectives: Know what you want to learn and why.
- Choose the Right Methods: Tailor your approach to your goals and resources.
- Involve Stakeholders: Keep the team informed and involved throughout the process.
- Iterate Based on Findings: Use insights to refine and test designs.
- Respect Participant Time: Ensure a smooth and respectful research experience.
Recommended Resources
To deepen your understanding of user research, explore these valuable resources:
- NNGroup’s Guide to User Research
- Interaction Design Foundation: User Research Methods
- Springboard: What Does a UX Researcher Do?
Conclusion
User research is the foundation of user-centered design. By investing in understanding your users, you can create products that are not only functional but also delightful to use.
Whether you’re a seasoned designer or just starting, embracing user research will elevate your designs and ensure lasting impact.
If you want to continue reading about What Does a UX Researcher Do? please visit springboard.com