Understanding the Seven Fundamental Business Personalities
The concept of Business Model Archetypes provides a structured approach to understanding and designing business models.
These seven fundamental business personalities serve as a foundation for businesses to build upon, helping entrepreneurs, strategists, and innovators identify opportunities, pivot their strategies, and improve market positioning.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore each of these archetypes in detail, providing real-world examples, use cases, and insights into how businesses can leverage them for growth and innovation.
What Are Business Model Archetypes?
Business model archetypes are patterns or frameworks that categorize businesses based on their fundamental operational and value delivery mechanisms. By identifying an archetype that aligns with a business, organizations can gain strategic clarity, improve efficiency, and explore innovative directions.
The seven business model archetypes are:
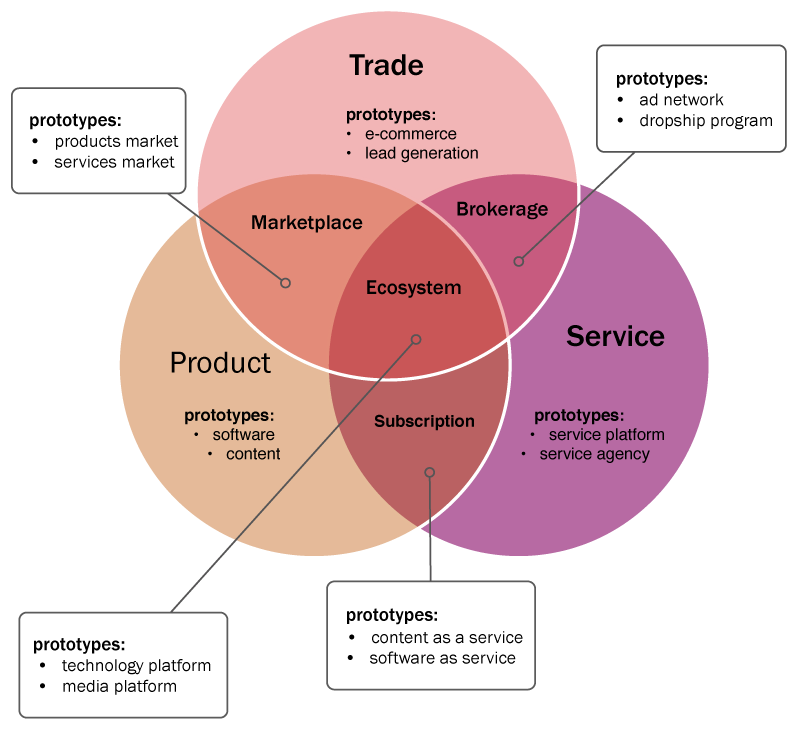
- Product Model
- Service Model
- Marketplace Model
- Subscription Model
- Community Model
- Ecosystem Model
- On-Demand Model
Each of these models represents a different way of delivering value, generating revenue, and engaging with customers. Let’s explore each in detail.
1. Product Model
Definition
The Product Model is one of the most traditional and well-known business models. It revolves around creating and selling tangible or digital products to customers in exchange for a one-time or recurring payment.
Characteristics
- Focuses on the development and distribution of a physical or digital product.
- Revenue comes from direct sales, licensing, or wholesaling.
- Requires inventory management, manufacturing, and distribution channels.
Examples
- Apple (Selling iPhones, MacBooks, and accessories)
- Nike (Footwear and sports apparel)
- Adobe (Software like Photoshop and Illustrator)
Best Use Cases
- Businesses that design and manufacture products.
- Companies that offer downloadable or SaaS-based software solutions.
2. Service Model
Definition
The Service Model focuses on offering expertise, labor, or a specialized service to customers. Revenue is typically generated through hourly billing, fixed contracts, or performance-based pricing.
Characteristics
- Intangible value through expertise and labor.
- Revenue from service fees, retainers, or project-based contracts.
- High customer engagement and customization potential.
Examples
- Consulting firms (McKinsey, Deloitte)
- Freelance services (Fiverr, Upwork)
- Healthcare and legal services (Doctors, Lawyers)
Best Use Cases
- Companies that offer custom solutions tailored to individual clients.
- Organizations where human expertise and skills drive value.
3. Marketplace Model
Definition
The Marketplace Model acts as an intermediary platform where buyers and sellers meet to exchange goods or services.
Characteristics
- Facilitates transactions between multiple parties.
- Revenue comes from commissions, listing fees, or membership fees.
- Relies on a strong network effect to scale.
Examples
- Amazon (E-commerce marketplace)
- eBay (Auction-based marketplace)
- Airbnb (Vacation rental marketplace)
Best Use Cases
- Businesses that connect suppliers and consumers.
- Platforms that enable peer-to-peer transactions.
4. Subscription Model
Definition
The Subscription Model provides continuous access to products or services in exchange for a recurring fee.
Characteristics
- Generates predictable and stable revenue.
- Encourages long-term customer relationships.
- Requires strong customer retention strategies.
Examples
- Netflix (Streaming entertainment)
- Spotify (Music subscription service)
- Amazon Prime (Membership-based benefits)
Best Use Cases
- Businesses offering digital content or ongoing services.
- Organizations focusing on customer retention and engagement.
5. Community Model
Definition
The Community Model builds and monetizes a dedicated user base around shared interests, knowledge, or experiences.
Characteristics
- Revenue generated from membership fees, ads, donations, or premium content.
- Strong focus on engagement and user-generated content.
- Leverages network effects for growth.
Examples
- Reddit (User-driven forums and discussions)
- Facebook Groups (Social communities and networking)
- Patreon (Creator monetization through memberships)
Best Use Cases
- Companies that create or curate community-driven experiences.
- Platforms focused on niche audiences.
6. Ecosystem Model
Definition
The Ecosystem Model integrates multiple products, services, or platforms into a unified experience.
Characteristics
- Revenue from cross-selling, integrations, and partnerships.
- Encourages customer lock-in and increased lifetime value.
- Creates a self-sustaining digital or physical environment.
Examples
- Apple Ecosystem (Mac, iPhone, iPad, iCloud, App Store)
- Google Services (Search, Ads, Cloud, YouTube, Android)
- Microsoft (Windows, Office, Azure, LinkedIn)
Best Use Cases
- Businesses with multiple interlinked products and services.
- Companies that benefit from customer retention and ecosystem lock-in.
7. On-Demand Model
Definition
The On-Demand Model provides instant access to products or services through digital platforms and apps.
Characteristics
- Real-time delivery of products or services.
- Revenue from transaction fees, surge pricing, or subscriptions.
- Requires strong operational infrastructure.
Examples
- Uber (Ride-sharing services)
- DoorDash (Food delivery)
- Fiverr (Freelance gig economy)
Best Use Cases
- Businesses that fulfill immediate customer needs.
- Companies with scalable logistics and supply chains.
Conclusion
Understanding and leveraging the right business model archetype can significantly impact an organization’s success. By identifying where a company fits within these archetypes, businesses can refine their strategies, optimize operations, and uncover new opportunities for growth.
Whether you’re an entrepreneur, a product strategist, or a business development leader, recognizing these archetypes can serve as a powerful strategic tool to stay ahead in a competitive market.
For further insights on business model innovation, visit:
What business model archetype does your company follow? Let us know in the comments!