Apple, a name synonymous with cutting-edge technology and iconic design, has cultivated a devoted following that transcends mere product loyalty.
Users often describe an emotional connection with their Apple devices, a testament to the company’s unique approach to product development.
This wasn’t always the case. A period of struggle in the late 80s and early 90s threatened Apple’s very existence.
This post, drawing upon insights from Dr. Rafiq Elmansy’s analysis of Apple’s resurgence, delves into the pivotal role of Design Thinking and innovation in transforming Apple from a company on the brink to a global powerhouse.
We will explore Apple’s journey, dissecting the challenges it faced and how the strategic implementation of design thinking principles, championed by Steve Jobs, fueled its remarkable comeback.
The Dark Days: Apple’s Struggle (1985-1997)
Apple’s early success stemmed from its pioneering personal computer and the innovative Apple OS. However, the forced departure of Steve Jobs in 1985 marked the beginning of a turbulent era. Without a clear direction, Apple floundered, grappling with:
- Leadership Instability: Frequent changes in executive teams led to inconsistent strategies and a lack of long-term vision.
- Competitive Pressure: The rise of IBM and the burgeoning PC market intensified competition, leaving Apple struggling to differentiate itself.
- Strategic Confusion: Debates over licensing the Apple OS created internal conflict and blurred the company’s competitive positioning.
- Product Failures: Despite occasional successes like the PowerBook, numerous product flops, most notably the Newton PDA, eroded consumer confidence.
- Brand Dilution: The lack of a cohesive product strategy resulted in market confusion and a weakened brand identity.
This period highlighted a critical need for a renewed focus on innovation and a customer-centric approach to product development.
Design Thinking: The Catalyst for Innovation and Change
Design thinking, a human-centered approach to innovation, provided the framework for Apple’s revitalization. As Tim Brown, CEO of IDEO, articulates,
“Design thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation that draws from the designer’s toolkit to integrate the needs of people, the possibilities of technology, and the requirements for business success.”
Steve Jobs understood that design was more than just aesthetics.
“Most people make the mistake of thinking design is what it looks like. People think it’s this veneer — that the designers are handed this box and told, ‘Make it look good!’ That’s not what we think design is. It’s not just what it looks like and feels like. Design is how it works.”
This philosophy became the cornerstone of Apple’s product development process.
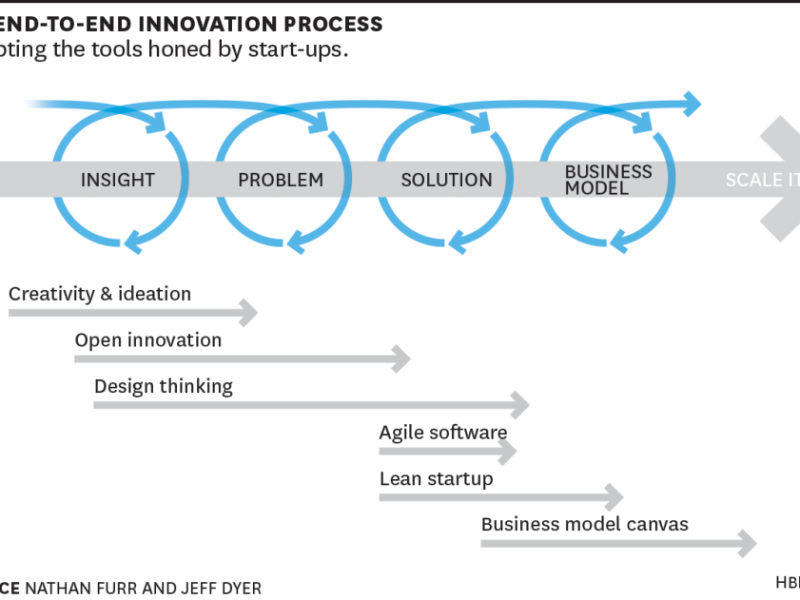
Design thinking methodologies, such as the IDEO Design Thinking model and the d.school model, emphasize three core elements:
- User Desirability: Understanding and addressing user needs through empathy and user-centered research. This involves creating products that solve real problems and enhance the user experience.
- Market Viability: Developing a sound business strategy that considers market dynamics, target audience, and competitive landscape. Tools like the Business Model Canvas and SWOT analysis are crucial in this process.
- Technological Feasibility: Leveraging technology to create innovative products that are not only desirable but also technically achievable. This includes exploring new technologies and incorporating them into the design and development process.
“Think Different”: The Apple Innovation and Renaissance
Jobs’ return to Apple in 1997 marked a turning point. He instilled a new culture centered around design thinking principles, prioritizing:
- User-Centricity: Focusing on user needs and desires above all else. Apple products are designed to seamlessly integrate into users’ lives, simplifying complex tasks and enhancing their overall experience.
- Empathy-Driven Design: Cultivating a deep understanding of users and their motivations. Apple strives to create products that users not only need but also love.
- Holistic Design: Considering both the form and function of a product. Apple products are renowned for their elegant aesthetics and intuitive functionality.
- Simplicity and Usability: Prioritizing ease of use and intuitive design. Apple products are designed to be accessible to a wide range of users, regardless of their technical expertise.
This philosophy is evident in Apple’s product strategy, which focuses on delivering a holistic user experience rather than simply packing in the latest features.
The iMac, for example, was lauded not just for its sleek design but also for its quiet operation, fast wake-up, superior sound, and high-quality display.
Key Elements of Apple’s Design Thinking Strategy:
- Excellence in Execution: Jobs streamlined operations, consolidating product lines, closing divisions, and outsourcing manufacturing to improve efficiency and focus on core competencies.
- Platform Strategy: Developing a cohesive ecosystem of interconnected products that work seamlessly together. This strategy fosters user loyalty and encourages the adoption of multiple Apple devices.
- Iterative Customer Involvement: Incorporating user feedback throughout the design and development process. Usability testing and user-centered design principles are integral to Apple’s product development cycle.
- Emphasis on Aesthetics: Creating visually stunning products that are as pleasing to the eye as they are functional. Apple’s commitment to design extends to every aspect of its products, from the materials used to the packaging.
The Power of Innovation:
Apple’s journey demonstrates the transformative power of design thinking and innovation. By placing the user at the heart of the product development process, Apple has consistently delivered groundbreaking products that have redefined entire industries.
The company’s success is a testament to the vision and leadership of Steve Jobs, who understood that design is not just about aesthetics but about creating products that seamlessly integrate into people’s lives and enhance their overall experience.
Conclusion:
Apple’s resurgence is a compelling case study in the power of Design Thinking. By embracing a user-centric approach, prioritizing simplicity and usability, and fostering a culture of innovation, Apple has transformed itself from a struggling company to a global leader.
This journey offers valuable lessons for businesses across all industries, demonstrating that a focus on design and innovation can be a powerful driver of success. Apple’s story is a reminder that true innovation stems from a deep understanding of user needs and a relentless pursuit of excellence in both form and function.
By continuing to prioritize design thinking principles, Apple is poised to remain at the forefront of innovation for years to come. This case study serves as an inspiration for businesses seeking to achieve sustainable growth and build lasting connections with their customers. Just as Apple has redefined the technology landscape, other companies can leverage design thinking to create innovative products and services that meet the evolving needs of their target markets.
The key is to embrace a human-centered approach, foster a culture of creativity, and never lose sight of the importance of design in shaping the user experience.

One thought on “Innovation at Apple: A Design Thinking Case Study”