A UX Designer’s Perspective
Innovation is at the core of business success, yet many companies struggle to define what it truly means. While some focus on groundbreaking products, others create value through services, processes, or financial models.
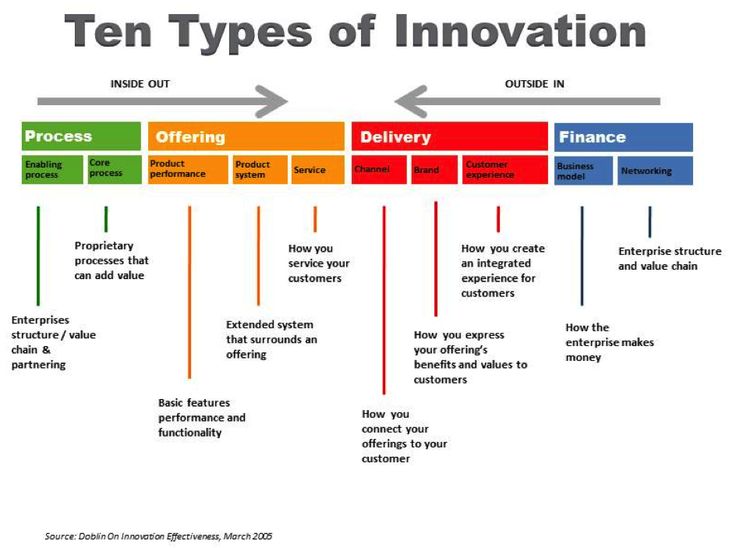
The “Ten Types of Innovation” framework, developed by Deloitte Digital, provides a structured approach to understanding how businesses can innovate beyond products alone.
In this article, we explore the ten types of innovation from the perspective of a Senior UX Designer with years of experience. We’ll examine how this framework applies to user experience (UX) design, product strategy, and business growth.
“Innovation is not just about technology; it’s about solving problems in meaningful ways.” – Doblin
Understanding the Ten Types of Innovation
The framework categorizes innovation into four broad areas: Process, Offering, Delivery, and Finance. Each area consists of specific innovation types that contribute to business growth and differentiation.
1. Process Innovation
Process innovation focuses on how a company delivers value, improves operations, and enhances efficiency.
1.1 Enabling Process
- Proprietary methods that streamline workflows and improve scalability.
- Example: Amazon’s AI-driven warehouse automation enhances order fulfillment speed.
1.2 Core Process
- Optimizing fundamental business functions for better efficiency.
- Example: Toyota’s Lean Manufacturing reduces waste while improving production quality.
UX Application:
- Leveraging design systems (e.g., Google’s Material Design) to create a seamless, scalable UX.
- Implementing AI-driven personalization to automate user interactions.
2. Offering Innovation
Offering innovations focus on the product or service itself and how it meets user needs.
2.1 Product Performance
- Enhancing product capabilities and performance.
- Example: Apple’s Retina Display set a new benchmark for screen resolution.
2.2 Product System
- Creating an ecosystem of complementary products.
- Example: Google’s suite of products (Docs, Drive, Meet, Gmail) offers seamless integration.
2.3 Service
- Innovating how services are delivered to enhance customer experience.
- Example: Netflix’s AI-driven content recommendation system.
UX Application:
- Designing frictionless onboarding experiences.
- Using UX research to refine product features based on real user data.
3. Delivery Innovation
Delivery innovations focus on how products reach customers and how brands engage users.
3.1 Channel Innovation
- New ways to distribute products or services.
- Example: Tesla’s direct-to-consumer sales model eliminates the need for dealerships.
3.2 Brand Innovation
- Enhancing how users perceive a brand.
- Example: Nike’s brand storytelling (e.g., “Just Do It”) builds emotional connections.
3.3 Customer Experience Innovation
- Creating an integrated, delightful experience.
- Example: Apple’s seamless ecosystem (iPhone, Mac, iCloud) ensures a smooth experience.
UX Application:
- Leveraging omnichannel experiences (web, mobile, voice interfaces).
- Designing for accessibility and inclusivity.
4. Finance Innovation
Finance innovations involve new ways to generate revenue and structure the business.
4.1 Business Model Innovation
- Changing how a business makes money.
- Example: Spotify’s Freemium Model enables both free and premium users.
4.2 Networking Innovation
- Leveraging partnerships and ecosystems.
- Example: Amazon Web Services (AWS) supports third-party developers and businesses.
UX Application:
- Subscription-based UX strategies (e.g., SaaS platforms with tiered pricing models).
- Using design thinking to create user-centered business models.
How UX Design Drives Innovation
User experience (UX) design plays a crucial role in all ten types of innovation. From designing better workflows to improving product usability, UX is a key differentiator in the innovation process.
Best Practices for UX-Driven Innovation
- User Research: Understanding real pain points through qualitative and quantitative research.
- Prototyping & Testing: Iterative design approaches to refine products.
- Data-Driven Design: Leveraging analytics to improve user engagement.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Working with business, tech, and marketing teams to align goals.
- Simplicity & Accessibility: Ensuring inclusivity in design choices.
Case Studies of Innovation in UX
Airbnb – Platform & Service Innovation
- Challenge: Traditional hotel booking systems lacked personalization.
- Innovation: Created a seamless peer-to-peer marketplace for accommodations.
- UX Impact: Personalized recommendations, trust-building UX elements (reviews, verified hosts).
Uber – Business Model & Delivery Innovation
- Challenge: Taxi services were inefficient and lacked transparency.
- Innovation: On-demand ride-sharing platform.
- UX Impact: GPS tracking, cashless payments, and real-time driver ratings.
Revolut – Finance & Product Innovation
- Challenge: Traditional banks offered limited digital experiences.
- Innovation: Mobile-first banking with AI-driven financial insights.
- UX Impact: Seamless transactions, real-time spending analytics, and multi-currency support.
Conclusion: The Future of Innovation in UX
Innovation is not limited to technology or products; it extends to every facet of a business. As UX designers, embracing the “Ten Types of Innovation” helps create more meaningful, inclusive, and impactful experiences for users.
Key Takeaways:
- Innovation is multi-dimensional, covering process, offering, delivery, and finance.
- UX design plays a pivotal role in shaping business innovations.
- Businesses that focus on user-centered innovation gain competitive advantages.
- Emerging technologies (AI, AR/VR, voice UI) will further drive UX-led innovation.
For organizations looking to scale innovation through UX, investing in research, design thinking, and data-driven strategies is the way forward.
Additional Resources
- Doblin’s Ten Types of Innovation: https://www.deloittedigital.com/us/en/accelerators/ten-types.html
- Four Paths to Business Model Innovation: https://hbr.org/2014/07/four-paths-to-business-model-innovation
- UX Design & Innovation Blog: https://www.nngroup.com/articles/
- The Role of UX in Digital Transformation: https://www.lionandmason.com/ux-blog/the-role-of-ux-in-digital-transformation-why-its-crucial-for-business-success/
By leveraging this framework, UX professionals and businesses can strategically innovate and remain at the forefront of industry trends.