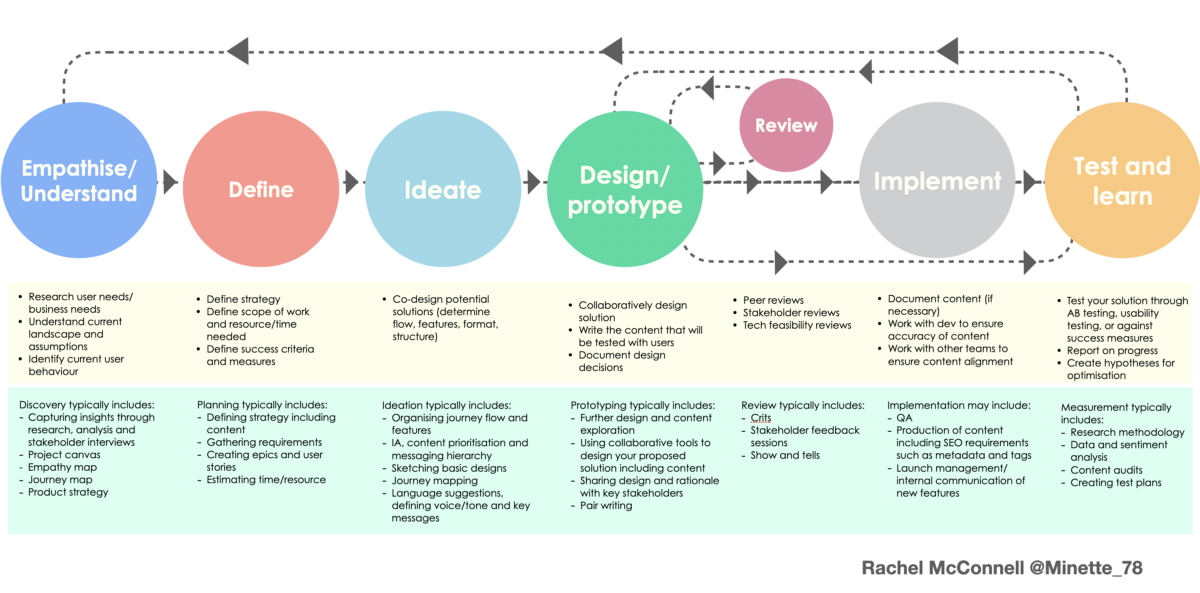
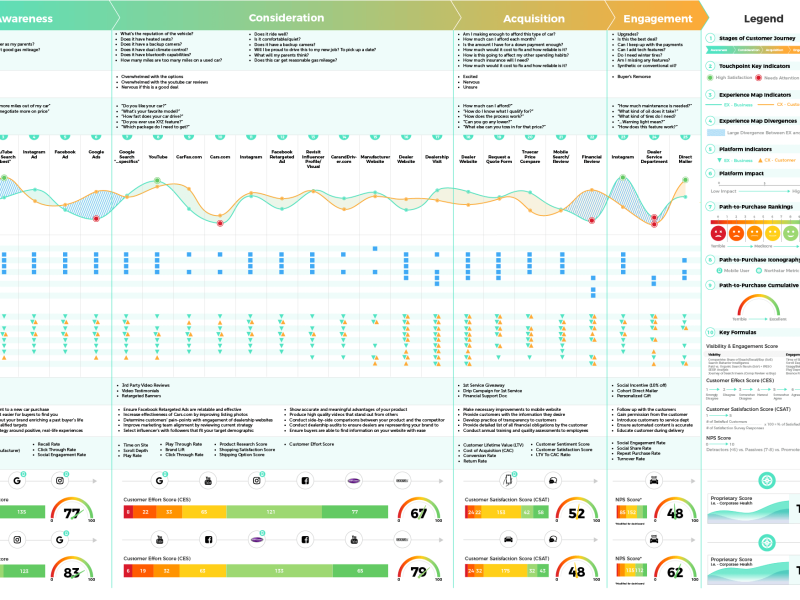
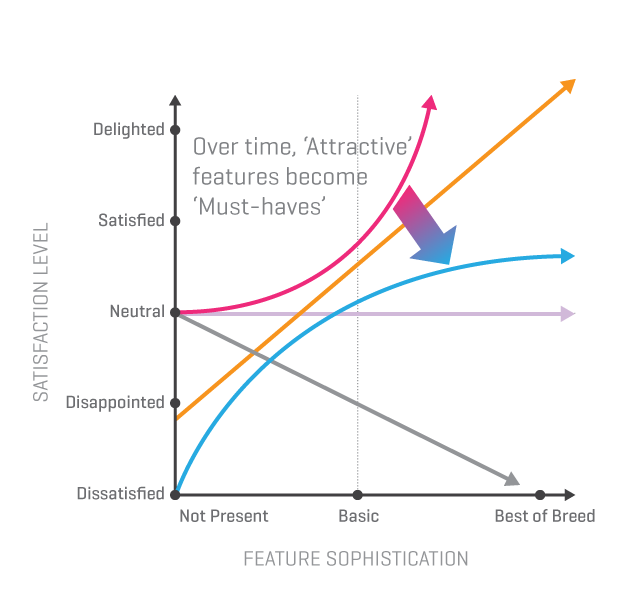
A Deep Dive into the Art and Science Behind Great Products
Product design is the intricate process of ideating, creating, and refining a new product or service to solve specific user problems or fulfill unmet needs.
While the concept might sound straightforward, its execution is a complex dance involving creativity, technology, and deep user understanding.
Whether you’re a beginner, an experienced developer, or an Amazon seller, product design principles can guide your journey toward successful product creation.
In this post, we’ll explore the essence of product design, its phases, and how it impacts business and users alike.
The Essence of Product Design
At its core, product design is about solving problems in effective, efficient, and aesthetically pleasing ways. This process isn’t limited to physical products but also extends to digital services and systems. Successful product design marries user needs with business goals and technological possibilities, ensuring the final product is both functional and delightful.
Product designers tackle questions like:
- What problems are users facing?
- How can we address these issues within technical and budget constraints?
- What design choices will resonate with the target audience?
The Phases of Product Design
1. Market Analysis and Research
Product design begins with understanding the market landscape. This involves gathering insights on:
- User needs and preferences
- Competitive products and their strengths/weaknesses
- Market trends and gaps
Tools like surveys, focus groups, and user interviews help paint a clear picture of the target audience’s desires and pain points.
2. Defining the Problem
With research insights in hand, the team defines the core problem the product will address. A well-articulated problem statement serves as the guiding light for the entire design process.
3. Conceptualization
In this phase, designers and engineers brainstorm ideas and generate potential solutions. Creativity takes center stage as teams:
- Sketch initial concepts
- Explore various design approaches
- Evaluate feasibility and potential impact
Iterative collaboration ensures ideas are refined and aligned with project goals.
4. Prototyping
Once a concept is selected, it’s time to bring it to life. Prototypes—ranging from simple sketches to high-fidelity models—allow teams to:
- Test functionality and usability
- Identify design flaws
- Gather early user feedback
Modern tools like Figma (for digital designs) and 3D printers (for physical products) accelerate the prototyping process.
5. Testing and Evaluation
Prototypes undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet design objectives. This stage includes:
- Functional testing to check performance
- Usability testing to assess user satisfaction
- Market testing to gauge potential success
Feedback gathered during testing informs necessary refinements.
6. Refinement and Finalization
Based on testing results, the design is further polished. This iterative process continues until the product meets all functional, aesthetic, and market requirements.
7. Production and Launch
The finalized design transitions to production. Designers often collaborate with manufacturing teams to ensure quality and consistency. A successful launch strategy includes marketing, distribution, and user onboarding.
Key Considerations in Product Design
1. User-Centric Approach
Understanding user behavior, preferences, and pain points is paramount. Empathy-driven design ensures products resonate with their intended audience.
2. Technical Feasibility
Designers must balance innovation with what’s technically achievable. Collaboration with engineers ensures ideas are practical and implementable.
3. Cost and Production Constraints
Budgets often dictate design choices. Efficient use of resources without compromising quality is a hallmark of great product design.
4. Aesthetic Appeal and Brand Identity
A product’s look and feel significantly influence its market success. Consistency with brand identity builds trust and recognition.
5. Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Products must adhere to industry standards and regulations to ensure user safety and avoid legal complications.
Product Design for Specific Audiences
For Beginners:
If you’re new to product design, start by learning the fundamentals of user research, prototyping, and iterative testing. Platforms like Coursera and Udemy offer excellent courses tailored for beginners.
For Experienced Developers:
Seasoned professionals can refine their skills by exploring advanced methodologies like design thinking and lean UX. Books such as “Don’t Make Me Think” by Steve Krug provide valuable insights.
For Inventors:
Focus on validating your ideas through rapid prototyping and user feedback. Learn about manufacturing processes and sales strategies to bridge the gap between concept and market-ready product.
For Amazon Sellers:
Differentiation is key. Consider introducing unique designs that address specific customer needs. Utilize customer reviews to identify gaps and opportunities for improvement.
Strategies to Boost Impact
- Influence Stakeholders: Great product designers excel at communicating ideas and rallying support. Use data-driven storytelling to demonstrate the value of your designs.
- Expand Your Career: Join companies that align with your values and offer growth opportunities. Networking with industry peers can open doors to exciting projects.
- Attract Opportunities: Building a strong personal brand through platforms like LinkedIn and Behance can increase visibility and credibility.
- Learn Continuously: Stay updated with the latest tools and trends in product design. Resources like Smashing Magazine and UX Collective are invaluable.
Practical Lessons from Leading Companies
Facebook:
The company’s design team emphasizes rapid prototyping and user testing to refine features like News Feed and Messenger.
LinkedIn:
By prioritizing user feedback, LinkedIn’s design team ensures its products address professional needs effectively.
Conclusion
Product design is a dynamic field that blends creativity, technical expertise, and user empathy. By understanding the phases of product design and leveraging best practices, anyone can create impactful products that resonate with their audience.
Whether you’re crafting your first product or refining your approach as a seasoned professional, the principles of product design remain consistent: empathize, innovate, and iterate. With the right tools and mindset, you can transform ideas into products that not only meet market needs but also delight users.
References
- Coursera: Product Design
- Don’t Make Me Think by Steve Krug
- Smashing Magazine
- UX Collective
- LinkedIn Design Blog
- Figma
- Amazon Seller Central
The image above belongs to “Content in the product design process — articulating our role“.