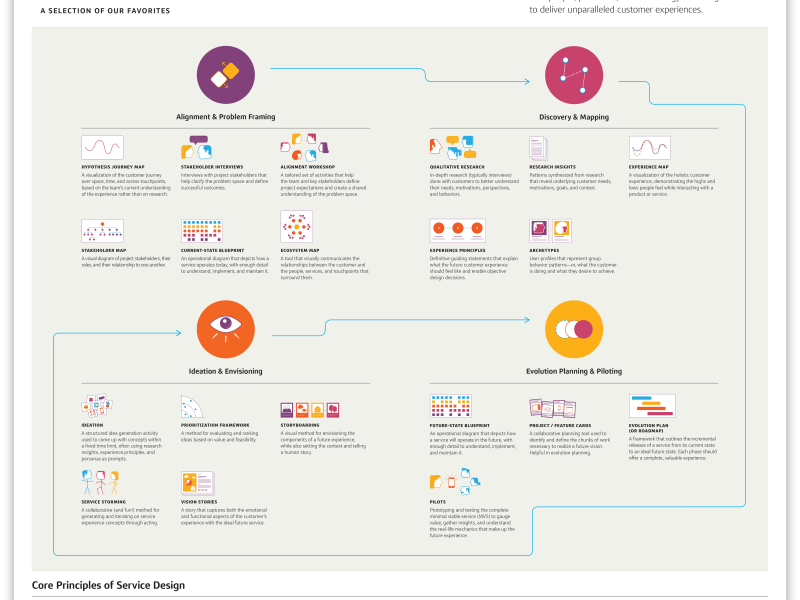
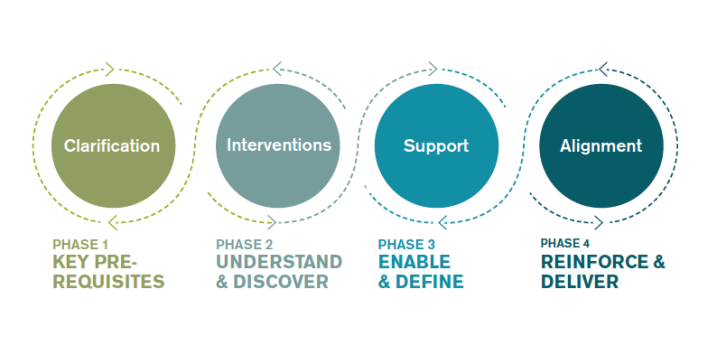
A Comprehensive Guide on Service Design
Service design is a dynamic and essential discipline that focuses on designing and delivering services that meet the needs and expectations of both users and business stakeholders.
In today’s competitive landscape, where user experience and customer satisfaction are paramount, service design has emerged as a key tool for organizations looking to innovate and create value.
In this post, we will explore what service design is, its core principles, processes, and why it’s crucial for businesses.
We’ll also provide actionable insights for organizations and professionals aiming to leverage service design for success.
What is Service Design?
Service design is the process of planning and organizing people, infrastructure, communication, and material components of a service to improve its quality and the interaction between the service provider and its customers. It combines principles from disciplines like Design Thinking, User Experience (UX) design, human-computer interaction, and service management to create solutions that are functional, usable, desirable, and accessible.
At its core, service design:
Addresses the needs of users and stakeholders.
Aims to create services that are efficient, effective, and enjoyable.
Focuses on innovation by solving complex challenges through collaboration.
Why is Service Design Important?
Service design plays a critical role in delivering exceptional user experiences. It ensures that services are aligned with user needs and business goals. By taking a holistic approach, organizations can:
Enhance User Experience: Service design ensures every touchpoint is optimized for the user.
Increase Efficiency: Well-designed services streamline operations, reducing costs and improving performance.
Drive Innovation: By addressing complex challenges, service design fosters creativity and innovation.
Build Brand Loyalty: Exceptional services create positive user experiences, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
Key Principles
Service design is grounded in several key principles that guide its practice:
User-Centered: Focus on understanding and addressing the needs, desires, and pain points of users.
Co-Creation: Involve stakeholders, including users, in the design process to ensure diverse perspectives.
Holistic Thinking: Consider the entire service ecosystem, including people, processes, and technology.
Iterative Process: Continuously prototype, test, and refine services based on feedback.
Evidence-Based: Use data and research to inform decisions and validate design solutions.
The Service Design Process
Service design follows a structured process to ensure that services are user-centered, efficient, and aligned with business goals. Below are the typical steps:
1. Define the Problem and Identify User Needs
Understanding the problem is the first step. Conduct research to gather insights into user needs, preferences, and pain points. Methods include:
Interviews and Surveys: Collect qualitative and quantitative data.
Focus Groups: Engage with users to explore their perspectives.
Journey Mapping: Visualize the user’s experience to identify gaps and opportunities.
2. Develop a Service Concept
Create a high-level description of the service that outlines:
Purpose: What problem does it solve?
Key Features: What functionalities will it include?
Benefits: How does it add value to users and stakeholders?
The service concept should align with the organization’s objectives while being rooted in user research.
3. Prototype and Test
Prototyping involves creating tangible representations of the service, such as mock-ups, wireframes, or even role-playing scenarios. Testing these prototypes with users helps:
Validate assumptions.
Identify usability issues.
Gather actionable feedback for improvement.
4. Implement and Manage the Service
Implementation requires careful planning and coordination. Develop a detailed plan that includes:
Service Delivery Plan: Outlines how the service will be delivered to users.
Operational Guidelines: Define the processes, roles, and responsibilities.
Once the service is live, continuously monitor and evaluate its performance. Use metrics and user feedback to identify areas for improvement.
Real-World Examples
1. Uber’s Seamless Ride Experience
Uber’s service design integrates technology, user interface, and logistics to create a frictionless experience for riders and drivers. By focusing on user needs, they’ve optimized booking, payments, and real-time tracking.
2. Banking Self-Service Kiosks
Banks have implemented self-service kiosks to reduce wait times and enhance customer satisfaction. These kiosks were designed after extensive user research to ensure intuitive interfaces and functionality.
3. Healthcare Appointment Systems
Hospitals have adopted Service Design to streamline appointment booking and reduce patient wait times. By involving stakeholders, they’ve developed solutions that improve both patient and staff experiences.
The Role of Technology
Technology is a powerful enabler of innovative service design. Tools like AI, IoT, and data analytics allow organizations to:
Personalize services.
Automate repetitive tasks.
Gain deeper insights into user behavior.
For example, chatbots powered by AI provide 24/7 customer support, enhancing user satisfaction while reducing operational costs.
Challenges identified
While service design offers immense benefits, it also comes with challenges:
Stakeholder Alignment: Balancing the needs of diverse stakeholders can be complex.
Resource Constraints: Limited budgets and time can hinder the design process.
Resistance to Change: Organizational inertia may slow down innovation.
Measuring Success: Identifying the right metrics to evaluate service effectiveness is crucial.
Best Practices
Involve Stakeholders Early: Ensure everyone’s input is considered from the beginning.
Leverage Data: Use data to inform and validate decisions.
Prototype Early and Often: Test ideas before full-scale implementation.
Focus on Accessibility: Design inclusive services that cater to diverse user groups.
Adopt an Agile Approach: Embrace flexibility and iteration to adapt to changing needs.
Learn More About the practice
If you’re looking to delve deeper into service design, check out the following resources:
Conclusion
Service design is more than just a buzzword; it’s a transformative approach that helps organizations create meaningful, user-centered services.
By embracing its principles and processes, businesses can deliver value, foster innovation, and build stronger relationships with their customers.
As service design continues to evolve, its importance in shaping the future of user experiences cannot be overstated.
Whether you’re a designer, manager, or business leader, understanding and applying service design can unlock new opportunities for success.
If you’re interested in learning more about Service Design, visit this NNg post – Service Design 101.