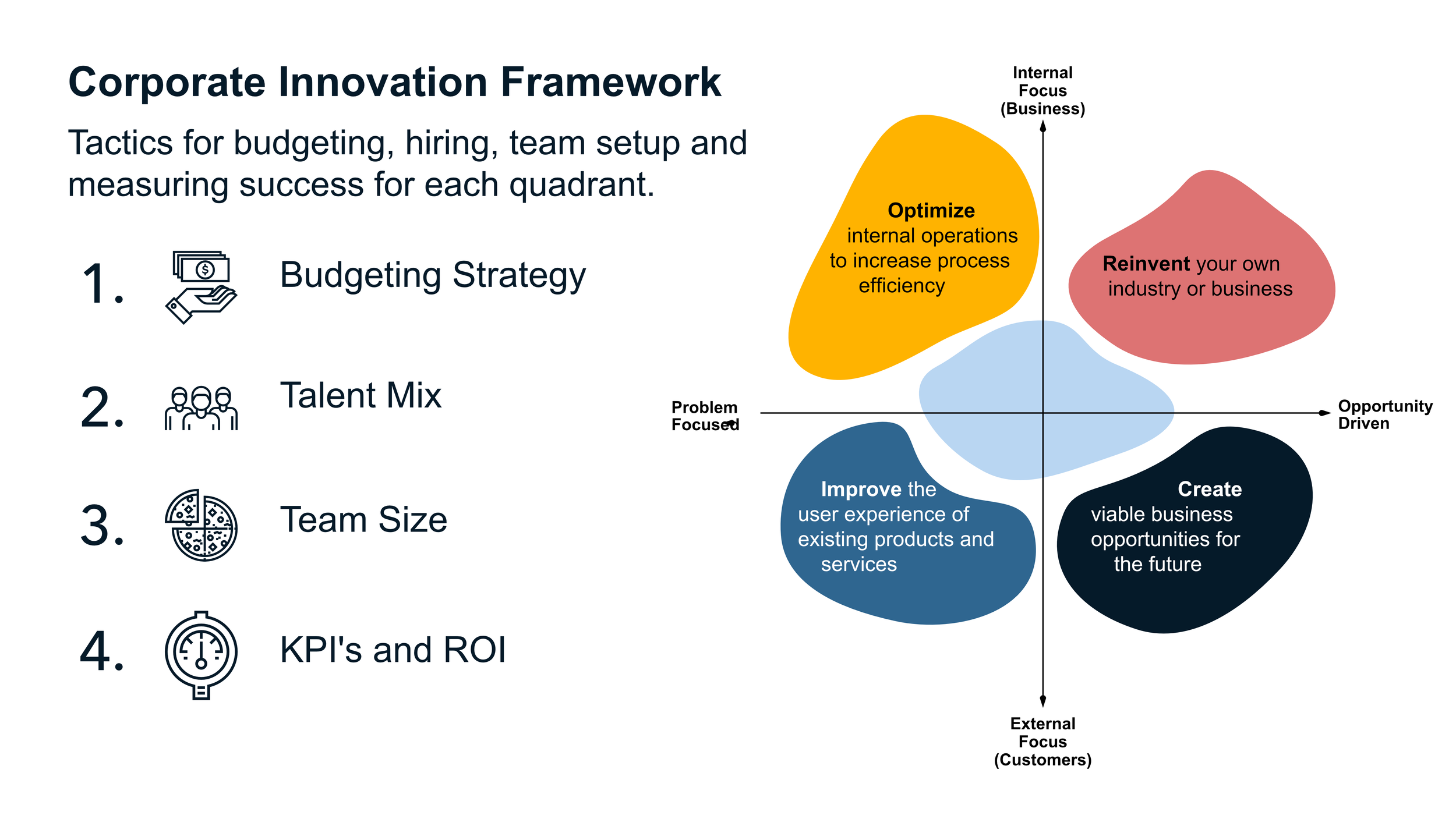
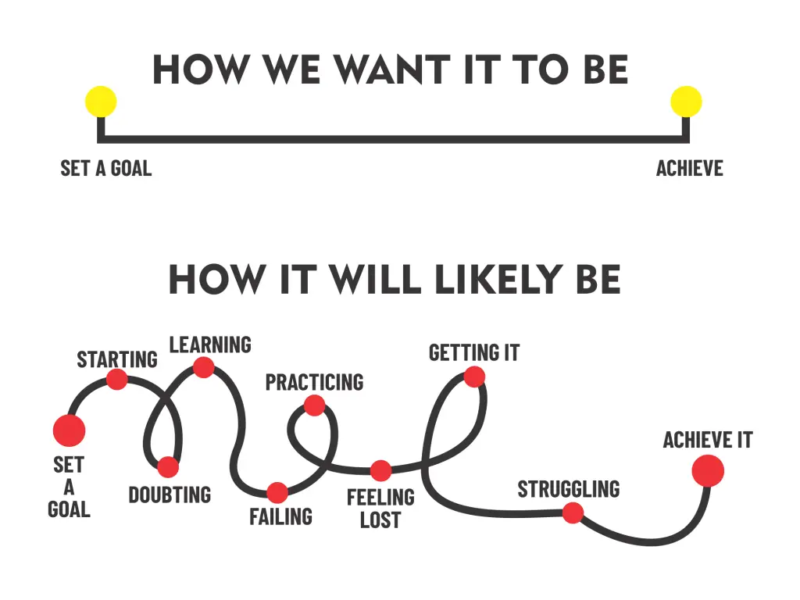
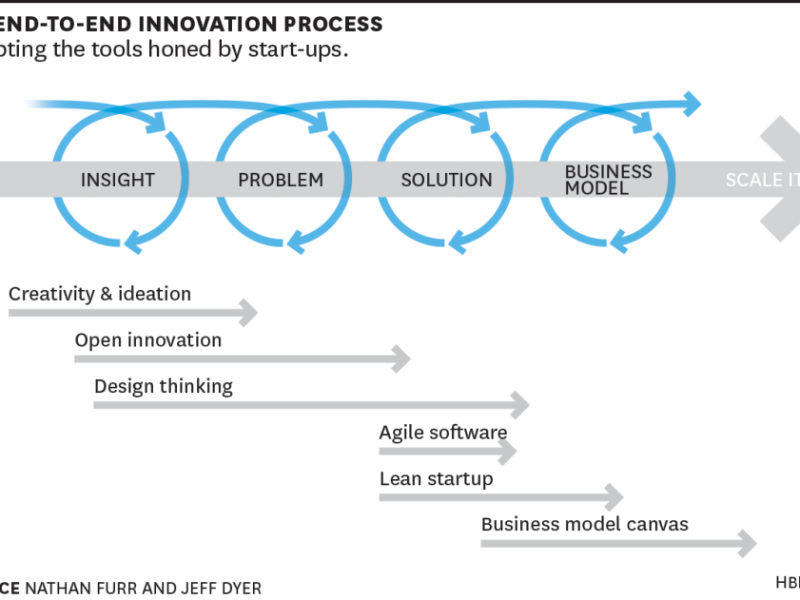
A Pathway to Human-Centered Solutions
In today’s fast-paced and competitive world, businesses are constantly seeking ways to stay ahead. At the core of this pursuit lies two transformative concepts: Innovation and Design Thinking.
Together, they form a powerful framework for developing new products and services that not only solve problems but also resonate deeply with the needs of users.
This blog explores how these two methodologies complement each other and outline actionable steps to integrate them effectively into organizational processes.
What is Innovation?
Innovation is the process of creating something novel or improving upon an existing idea, product, or service. It thrives on creativity, experimentation, and the willingness to explore uncharted territories. The outcomes of innovation can be groundbreaking, leading to new revenue streams, improved efficiency, or enhanced customer satisfaction.
What is Design Thinking?
Design Thinking is a human-centered approach to problem-solving that emphasizes:
- Empathy – Understanding user needs and pain points.
- Ideation – Generating creative solutions.
- Experimentation – Prototyping and testing ideas iteratively.
By focusing on the end-user, Design Thinking ensures solutions are not just innovative but also relevant and meaningful.
How Innovation and Design Thinking Work Together
The synergy between Innovation and Design Thinking is seamless. While Innovation provides the “how” of creating value, Design Thinking offers the “why” by keeping the user at the center. Here’s a step-by-step guide to integrating these methodologies:
1. Identify the Problem or Opportunity
The journey begins by pinpointing the challenge or opportunity to address. Use market research, customer feedback, and data analytics to:
- Uncover unmet needs.
- Spot trends or gaps in the market.
- Align opportunities with organizational goals.
Example: An e-commerce company noticing high cart abandonment rates could view this as an opportunity to streamline the checkout process.
2. Define the User and Their Needs
Understanding your user is critical. Conduct interviews, surveys, and observational studies to build a clear picture of:
- User demographics and behaviors.
- Pain points and desires.
- Existing solutions they interact with.
Tools to Use:
- Empathy maps.
- User personas.
- Journey mapping.
3. Generate Ideas
Empowered by user insights, ideate without limits. Foster creativity through:
- Brainstorming sessions.
- Design sprints.
- Cross-functional workshops.
The goal is to explore as many potential solutions as possible.
Tip: Avoid prematurely judging ideas to encourage free thinking.
4. Select and Refine Ideas
Evaluate generated ideas against three criteria:
- Feasibility: Can it be implemented?
- Desirability: Does it address user needs?
- Viability: Is it financially sustainable?
Refine top ideas into detailed concepts, incorporating feedback from stakeholders.
5. Prototype and Test
Bring ideas to life through rapid prototyping. Prototypes can be:
- Low-fidelity: Paper sketches or mockups.
- High-fidelity: Interactive digital models or functional builds.
Test these prototypes with real users to gather actionable feedback.
6. Iterate and Refine
Use testing insights to improve prototypes. This iterative process ensures the final solution is both functional and user-friendly.
Key Questions to Ask:
- What worked well?
- What needs improvement?
- What’s missing?
7. Launch and Evaluate
Introduce the final product or service to the market. Measure its success using:
- Customer satisfaction surveys.
- Usage analytics.
- Market impact studies.
Make post-launch adjustments based on user feedback and performance data.
The Role of an Innovation Squad
An Innovation Squad is a dedicated team tasked with driving innovation within an organization. These squads often consist of:
- Innovation Managers: Guide the team’s strategy and ensure alignment with business goals.
- Designers: Focus on user experience and aesthetics.
- Researchers: Gather and analyze user data.
- Technologists: Build and implement technical solutions.
- Business Strategists: Assess financial and market viability.
- Creative Problem-Solvers: Generate and refine innovative ideas.
Example in Action: An automotive company forms an Innovation Squad to explore electric vehicle solutions, combining expertise in engineering, user design, and market strategy.
Measuring Success with KPIs
To gauge the impact of an Innovation Squad, track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), such as:
- New Ideas Generated: Creativity and innovation levels.
- Prototypes Tested: Effective use of Design Thinking.
- Successful Launches: Market viability of products/services.
- Customer Satisfaction: User reception and feedback.
- Revenue Growth: Financial success of innovations.
- Time to Market: Efficiency of development processes.
Calculating ROI for Innovation Squads
Quantifying the return on investment (ROI) helps justify continued investment in innovation. Here’s how:
- Calculate Costs: Include salaries, tools, training, and other resources.
- Measure Benefits: Assess revenue generated, cost savings, and market impact.
- Formula:
ROI = (Benefits – Costs) / Costs × 100
Example: If an Innovation Squad costs $100,000 and generates $200,000 in benefits, the ROI is 100%.
Conclusion
Integrating Innovation and Design Thinking is not just a methodology but a mindset. By fostering creativity, empathy, and experimentation, organizations can:
- Solve complex problems.
- Enhance user satisfaction.
- Drive sustainable growth.
Whether you’re launching an Innovation Squad or refining your design processes, remember that user-centricity is the key to long-term success.
For more insights, tools, and real-world examples, visit Corporate Innovation: Team Setup, Budgeting Strategies, And ROI.