A Comprehensive Guide on What are the UX Design Ingredients
UX design (user experience design) is a multifaceted field requiring the integration of diverse inputs to create user-centric solutions.
The term “UX design ingredients” refers to the core elements that inform and shape the design process. These ingredients provide the foundation for building products and services that meet both user needs and business goals.
In this article, we will explore the key UX design ingredients, their significance, and how they work together to create impactful designs. By understanding these components, designers can craft effective, user-centered solutions.
The Core UX Design Ingredients
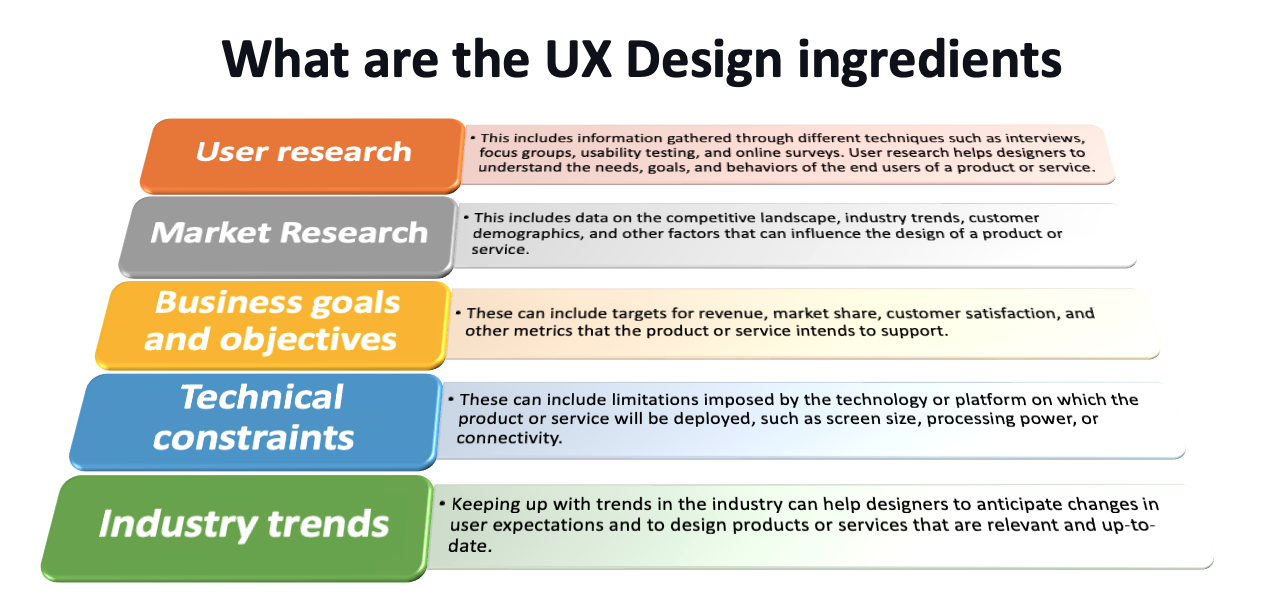
1. User Research
User research forms the cornerstone of the UX design process. It involves gathering and analyzing data about the needs, goals, and behaviors of end users. This data helps designers understand the context in which a product or service will be used, ensuring it is relevant and satisfying to the user.
Methods of User Research:
- Interviews: One-on-one conversations to uncover users’ needs, preferences, and behaviors.
- Focus Groups: Group discussions to explore diverse perspectives and delve deeper into specific topics.
- Usability Testing: Observing users interact with a product to identify issues and improve usability.
- Online Surveys: Collecting data quickly and inexpensively from a large user base.
Why It Matters: User research provides insights that shape design decisions, ensuring solutions are aligned with actual user needs rather than assumptions.
For an in-depth guide on user research, visit Nielsen Norman Group’s resources.
2. Market Research
Market research complements user research by focusing on external factors that influence product design, such as industry trends, customer demographics, and the competitive landscape.
Types of Market Research:
- Primary Research: Direct data collection via interviews, surveys, or focus groups.
- Secondary Research: Leveraging existing resources like industry reports and trade publications.
- Observational Research: Studying how users interact with products in real-world settings.
Why It Matters: Market research helps designers understand the broader context of the market, identify opportunities for differentiation, and align products with customer expectations.
For more insights on conducting market research, check out HubSpot’s market research guide.
3. Business Goals and Objectives
Business goals and objectives define what a product or service aims to achieve. These targets guide design decisions to ensure the product aligns with organizational priorities.
Key Business Goals in UX Design:
- Financial Goals: Revenue growth, profitability, or return on investment.
- Marketing Goals: Enhancing brand awareness, customer acquisition, or retention.
- Operational Goals: Improving efficiency, scalability, or productivity.
Why It Matters: Designers who understand business objectives can create solutions that deliver value to both the user and the organization.
Learn more about integrating business goals into UX design at Smashing Magazine.
4. Technical Constraints
Technical constraints refer to the limitations imposed by the technology or platform used for the product. Examples include screen size, processing power, connectivity, or software compatibility.
Common Technical Constraints:
- Device Capabilities: Designing for varying screen sizes and resolutions.
- Performance Limitations: Balancing features with processing power and battery usage.
- Platform Guidelines: Adhering to design standards for platforms like iOS or Android.
Why It Matters: Recognizing technical constraints early ensures designs are feasible and optimally utilize the platform’s capabilities. Creative solutions often emerge when working within these boundaries.
Explore best practices for designing within technical constraints at Material Design.
5. Industry Trends
Staying informed about industry trends enables designers to anticipate changes in user expectations and develop innovative solutions. Trends often reflect shifts in technology, consumer behavior, and market dynamics.
Key Industry Trends to Watch:
- Personalization: Delivering tailored experiences based on user data.
- Sustainability: Incorporating eco-friendly practices and materials.
- Voice Interfaces: Designing for voice-activated devices and services.
- AI Integration: Leveraging artificial intelligence for predictive and adaptive experiences.
Why It Matters: By staying current with trends, designers can create relevant and forward-thinking solutions that stand out in the marketplace.
Discover emerging UX trends at UX Collective.
Combining the Ingredients
The power of UX design lies in synthesizing these ingredients into a cohesive design process. Here’s how:
- Gathering Inputs: Use user research, market research, and business goals to form a comprehensive understanding of the design challenge.
- Analyzing Data: Identify patterns, opportunities, and constraints from the gathered information.
- Iterative Design: Develop prototypes and test them with users, refining the design based on feedback.
- Implementation: Collaborate with technical teams to ensure the design aligns with platform capabilities and business goals.
- Continuous Improvement: Monitor industry trends and user feedback post-launch to refine and enhance the product.
Conclusion
Understanding and utilizing the core ingredients of UX design is essential for creating successful user-centered products. User research, market research, business objectives, technical constraints, and industry trends each play a vital role in shaping the design process.
By synthesizing these components, designers can craft solutions that are not only functional and visually appealing but also meet user needs and business goals. Keep these ingredients in mind to elevate your UX design process and deliver impactful results.
For more on mastering UX design, explore Interaction Design Foundation and stay ahead in the ever-evolving field of user experience.
Want to learn more about UX Design ingredients? check out this “The top five UX Design ingredients a designer should always keep in their back pocket“.