Setting clear, actionable, and achievable goals is critical to the success of any UX project.
Without defined objectives, measuring progress, evaluating outcomes, or ensuring alignment with user and business needs becomes challenging.
That’s where the S.M.A.R.T. framework comes in. In this post, we’ll explore how to write S.M.A.R.T. goals for UX projects and why this approach can dramatically improve project outcomes.
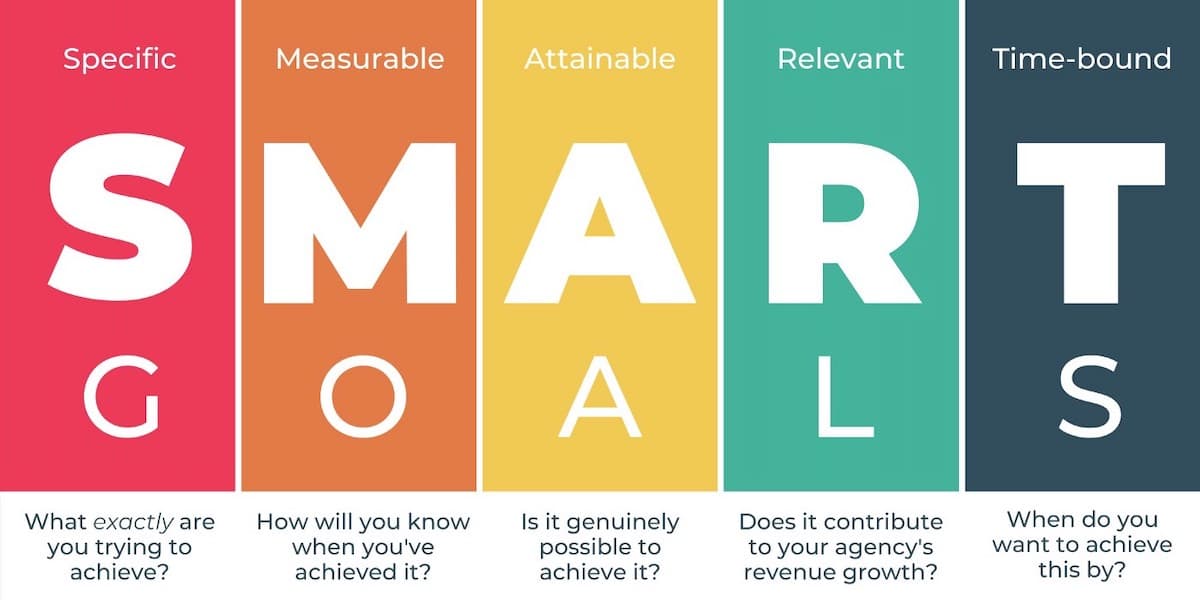
What Are S.M.A.R.T. Goals?
The S.M.A.R.T. framework provides a structured approach to goal setting. It ensures that every goal is:
- Specific: Clearly defined and focused on a particular outcome.
- Measurable: Quantifiable so progress can be tracked.
- Achievable: Realistic and feasible within the constraints of resources and time.
- Relevant: Aligned with broader organizational objectives and user needs.
- Time-bound: Set within a specific timeframe to ensure accountability.
Using this framework allows UX professionals to create actionable plans that align with project objectives while addressing user needs effectively.
Why S.M.A.R.T. Goals Matter for UX Projects
Clarity and Focus
S.M.A.R.T. goals eliminate ambiguity by providing a clear roadmap for what needs to be achieved and how to measure success. This is especially important in UX projects, where priorities can shift based on user feedback and stakeholder input.
Alignment with User Needs
UX projects aim to improve the user experience, but without clear goals, it’s easy to lose sight of the user’s perspective. S.M.A.R.T. goals ensure that user needs remain at the forefront.
Enhanced Collaboration
Clearly defined goals facilitate better communication among team members, stakeholders, and clients. When everyone understands the objectives, it’s easier to align efforts and resources.
Improved Accountability
By setting measurable and time-bound goals, teams can track progress, identify roadblocks, and celebrate achievements. This accountability fosters a culture of continuous improvement.
How to Write S.M.A.R.T. Goals for UX Projects
Let’s break down each component of the S.M.A.R.T. framework and how to apply it to UX projects.
1. Specific
The first step in setting S.M.A.R.T. goals is ensuring they are specific. A vague goal like “improve user experience” is hard to act upon. Instead, define the exact outcome you want to achieve.
Example: “Increase the website’s conversion rate by 20% within six months by simplifying the checkout process.”
This goal specifies the target (conversion rate), the improvement percentage (20%), the timeline (six months), and the method (simplifying the checkout process).
Tips:
- Use action verbs to describe what you aim to accomplish.
- Identify the specific problem or opportunity your goal addresses.
- Tailor the goal to align with user needs and project objectives.
2. Measurable
To evaluate success, goals must be measurable. Identify key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics relevant to your UX project.
Common UX Metrics:
- Task completion rate
- Conversion rate
- Click-through rate (CTR)
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Time on task
- User satisfaction ratings
Example: “Reduce the average time to complete the signup process from five minutes to three minutes within three months.”
This goal includes a specific metric (time to complete the signup process) and a target reduction (from five to three minutes).
Tips:
- Use tools like Google Analytics, Hotjar, or user testing platforms to track metrics.
- Regularly review progress and adjust as needed.
3. Achievable
Ambitious goals are great, but they must also be realistic. Setting unattainable objectives can demotivate teams and hinder progress.
Example: “Increase mobile app downloads by 15% over the next quarter through targeted in-app promotions and a redesigned app store listing.”
This goal considers available resources (targeted promotions and app store redesign) and sets a feasible target (15% increase).
Tips:
- Assess available resources, including budget, tools, and team capacity.
- Base your goals on research and past performance data.
4. Relevant
Goals should align with the project’s purpose and organizational objectives. Ask yourself whether achieving this goal will contribute to the overall mission.
Example: “Improve the task completion rate of the onboarding process by 10% within six months to enhance user retention.”
This goal is relevant because it directly impacts user retention, a key objective for most UX projects.
Tips:
- Regularly revisit the project’s mission to ensure alignment.
- Involve stakeholders to validate the relevance of your goals.
5. Time-bound
Deadlines create urgency and help teams stay on track. Without a timeline, projects can lose momentum or become open-ended.
Example: “Conduct five usability tests within the next two months to identify barriers in the checkout process.”
This goal specifies both the number of tests (five) and the deadline (two months).
Tips:
- Set milestones for long-term goals to track incremental progress.
- Use project management tools like Asana or Trello to manage timelines.
Applying S.M.A.R.T. Goals to Real-World UX Scenarios
Case Study 1: Redesigning an E-commerce Website
Goal: “Increase the e-commerce website’s conversion rate by 25% within six months by streamlining the product search and checkout processes.”
Approach:
- Conduct user research to identify pain points in the search and checkout flows.
- Implement A/B testing to validate design changes.
- Track conversion rates weekly and adjust strategies as needed.
Case Study 2: Improving a Mobile App’s Usability
Goal: “Reduce the average time to complete key tasks by 15% within three months through UI improvements and in-app guidance.”
Approach:
- Perform usability testing to pinpoint bottlenecks.
- Redesign the UI based on test findings.
- Use analytics to monitor task completion times post-launch.
Tools and Resources for S.M.A.R.T. Goal Tracking in UX Projects
Analytics Platforms
- Google Analytics: Track website performance metrics like bounce rate and conversion rate.
- Mixpanel: Analyze user behavior and retention rates.
User Testing Tools
- Hotjar: Gather heatmaps, session recordings, and user feedback.
- UserTesting: Conduct remote usability testing with real users.
Project Management Tools
- Asana: Manage tasks, deadlines, and milestones.
- Trello: Create visual workflows for goal tracking.
Design Collaboration Tools
- Figma: Collaborate on design iterations in real time.
- InVision: Share prototypes and gather stakeholder feedback.
Conclusion
S.M.A.R.T. goals provide a robust framework for planning and executing UX projects. By setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound objectives, UX teams can stay focused, aligned, and accountable. This structured approach not only enhances project outcomes but also ensures that user needs and business goals are met effectively.
By leveraging the tips, examples, and tools outlined in this guide, you can start writing S.M.A.R.T. goals that drive impactful results in your UX projects.
For more insights and best practices in UX design, check out these resources:
- Nielsen Norman Group – UX Metrics and ROI
- Smashing Magazine – Goal Setting for UX Designers
- UX Design Institute – Importance of Setting UX Goals
- Interaction Design Foundation – Usability Metrics
By adopting S.M.A.R.T. goals, you’re setting yourself and your UX projects up for success. Start applying this framework today and see the difference it makes!
The image belongs to “How to write effective SMART goals“