Gain Competitive Advantage through the Imperative of Innovation.
In today’s hyper-competitive market, businesses must innovate or risk obsolescence. A 2023 Gartner report reveals that 76% of organizations prioritize agility and experimentation to outpace competitors.
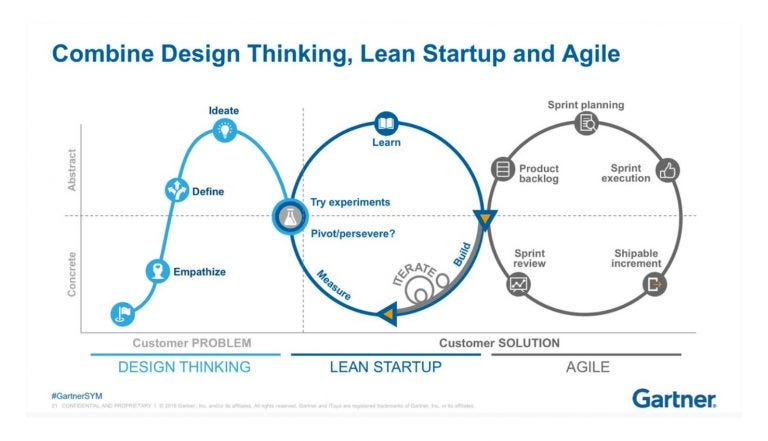
Yet, innovation isn’t about guesswork—it’s about systematically combining Design Thinking, Lean Startup, and Agile methodologies to align customer needs with rapid execution.
This post unpacks how these frameworks intersect, offering a blueprint for embedding continuous learning and experimentation into your DNA and supporting you on how to gain a Competitive Advantage.
Section 1: Understanding the Core Methodologies
1.1 Design Thinking: Human-Centered Problem Solving
Design Thinking starts with empathy—understanding the customer’s problem before jumping to solutions. The five phases include:
- Empathize: Immerse in the user’s world through interviews and observations.
- Define: Synthesize insights into a clear problem statement.
- Ideate: Brainstorm creative solutions.
- Prototype: Build low-fidelity models.
- Test: Validate with real users.
Example: Airbnb used Design Thinking to pivot from near-failure to a $113B valuation by redesigning their platform around user trust.
SEO Tip: For tools, explore IDEO’s free Design Thinking toolkit.
1.2 Lean Startup: Build-Measure-Learn
Eric Ries’ Lean Startup emphasizes rapid experimentation to validate customer solutions. Key principles:
- MVP (Minimum Viable Product): Launch quickly to test hypotheses.
- Pivot/Persevere: Use data to decide whether to change direction or double down.
- Innovation Accounting: Track progress with actionable metrics.
Case Study: Dropbox used an MVP (a explainer video) to validate demand before building their product, securing 75,000 sign-ups overnight.
Resource: Read Ries’ The Lean Startup for experimentation frameworks.
1.3 Agile: Iterative Delivery
Agile focuses on delivering shippable increments through time-boxed sprints. Key rituals:
- Sprint Planning: Define goals and tasks.
- Daily Standups: Align teams.
- Sprint Review: Demo outcomes.
- Retrospective: Reflect and improve.
Statistic: Teams using Agile are 28% more productive and 37% faster to market.
Tool: Use Jira or Trello for backlog management.
Section 2: Synergies Between Design Thinking, Lean Startup, and Agile
These methodologies form a cohesive innovation engine:
- Design Thinking identifies the right problem.
- Lean Startup tests the right solution.
- Agile scales the solution efficiently.
SPRAT Framework (Sprint, Plan, Review, Adapt, Test):
- Aligns sprint cycles (Agile) with experimentation (Lean) and user feedback (Design Thinking).
Section 3: A Step-by-Step Integration Playbook
3.1 Phase 1: Discover (Empathize & Define)
- Conduct user interviews and create personas.
- Tools: Miro for empathy mapping.
3.2 Phase 2: Experiment (Ideate & MVP)
- Run design sprints to prototype ideas.
- Example: Google Ventures’ 5-day sprint framework.
3.3 Phase 3: Execute (Sprint Planning & Review)
- Break down MVPs into user stories for the sprint backlog.
- Measure success with KPIs like customer retention.
3.4 Phase 4: Learn (Pivot/Persevere)
- Use A/B testing and analytics tools like Hotjar.
Section 4: Real-World Success Stories
- IBM: Reduced design costs by 33% with Agile + Design Thinking.
- Spotify: Uses squad frameworks (Agile) and continuous experimentation to stay ahead.
Section 5: Overcoming Challenges
- Siloed Teams: Foster cross-functional collaboration.
- Fear of Failure: Celebrate “learning launches” over perfect outcomes.
Conclusion: Build a Culture of Experimentation
Competitive advantage isn’t static—it’s earned through relentless learning. Start small: run a design sprint, launch an MVP, and iterate fearlessly.