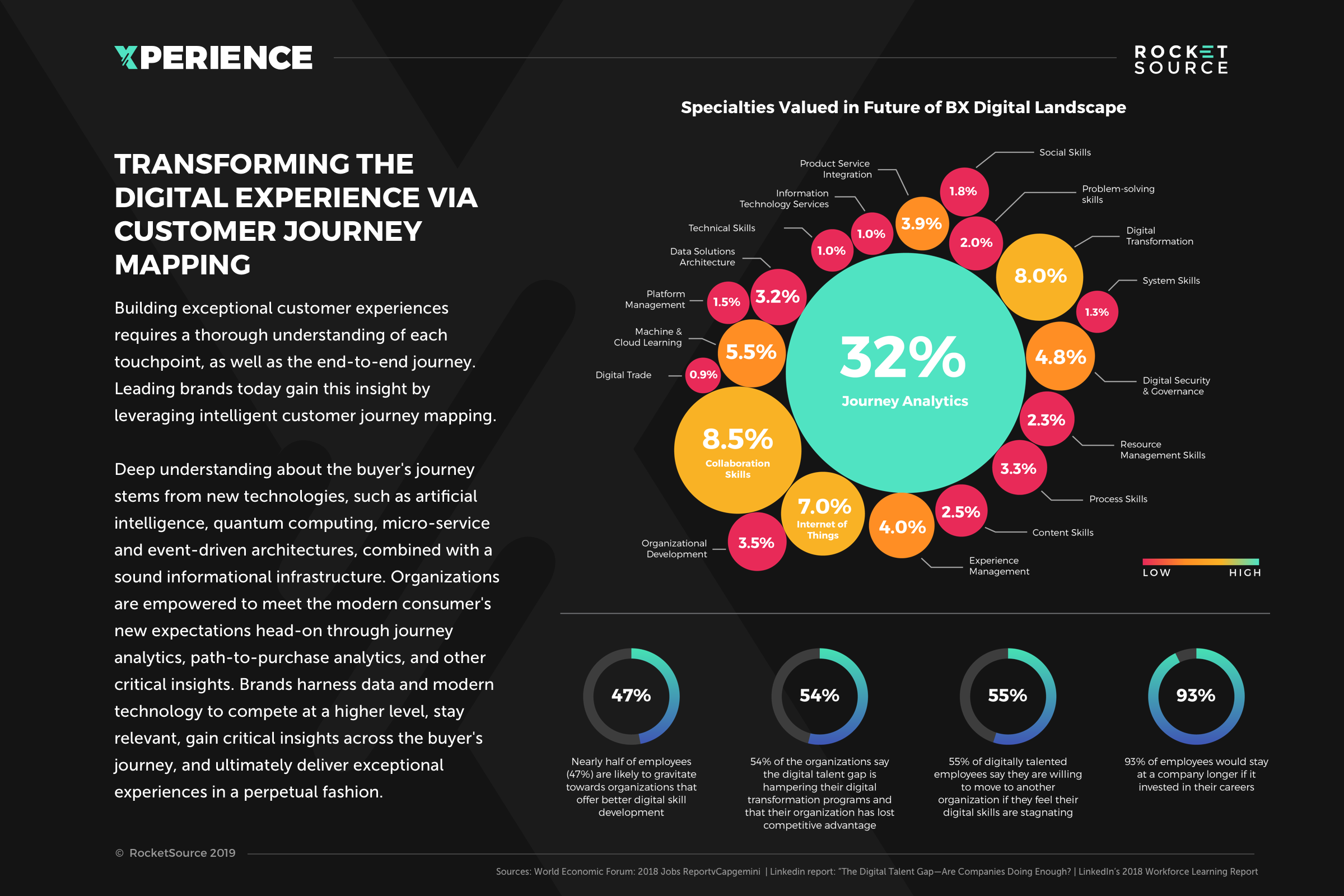
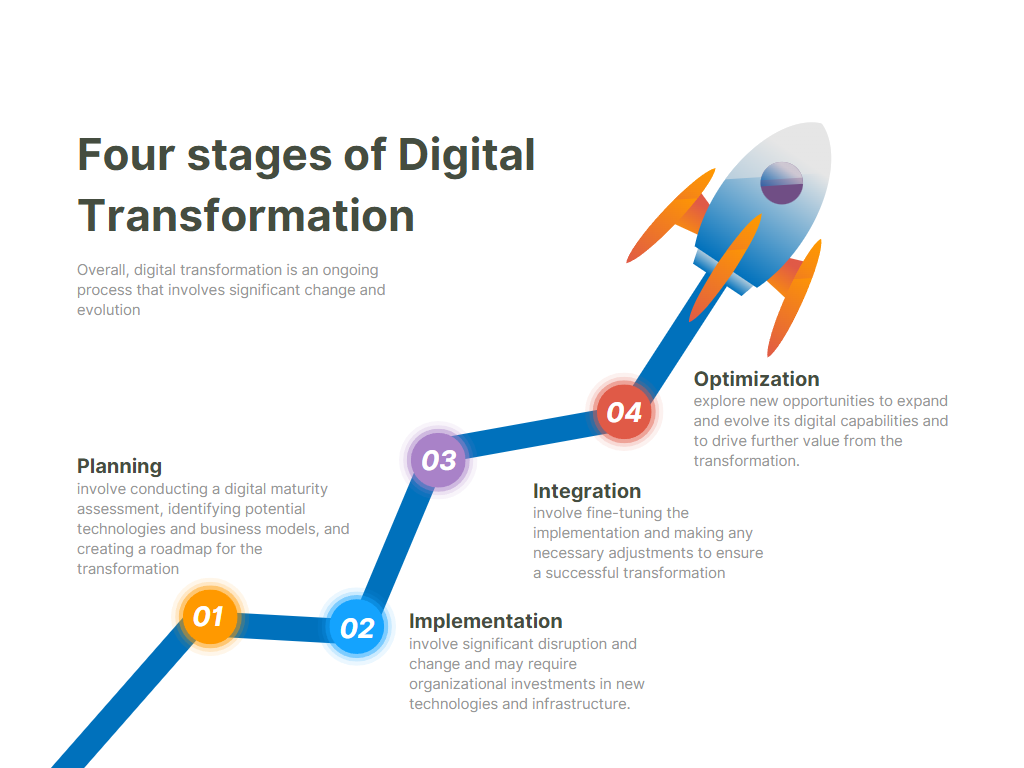
The Evolution of Customer Journey Mapping
The New Competitive Battlefield: Why Traditional Mapping No Longer Suffices
Customer journey mapping has undergone a radical transformation. What was once a static exercise involving sticky notes and whiteboards has evolved into a dynamic, AI-powered intelligence system that forms the very foundation of competitive digital experience . In today’s landscape, where 76% of consumers express frustration when they don’t receive personalized experiences, organizations can no longer rely on periodic, assumption-based mapping exercises. The digital economy now comprises approximately 15% of global GDP—about $16 trillion—making the stakes for getting customer experiences right higher than ever.
The fundamental shift we’re witnessing moves journey mapping from a retrospective documentation exercise to a predictive, actionable intelligence framework. Modern customers don’t just expect seamless experiences; they demand anticipatory service that understands their needs before they articulate them. This requires a sophisticated approach that combines the nuanced understanding of human-centered design with the scalable pattern recognition of artificial intelligence .
In this comprehensive examination, we’ll explore how organizations can leverage advanced journey mapping to drive digital transformation, what tools and frameworks deliver actionable insights, and how to bridge the critical gap between data collection and meaningful customer connection. The organizations that master this balance—combining disciplined customer journey design, ethical data use, and empathy—will be the ones that dominate their markets in the coming years .
The AI Revolution in Customer Journey Mapping
Artificial intelligence has transformed customer journey mapping from a static snapshot into a living, breathing system that continuously evolves with customer behaviors. Unlike traditional mapping methods that captured moments in time, AI-powered mapping stitches together fragmented data points—every click, email open, chat message, and login—to create unified profiles that reveal patterns humans might never notice independently .
From Touchpoints to Journeys: The AI Difference
The fundamental shift AI enables is moving from isolated touchpoint optimization to holistic journey understanding. Where traditional mapping might identify that customers abandon carts at checkout, AI can detect that customers who read specific blog articles then engage with certain product features are 3x more likely to become brand advocates—and can proactively guide similar customers along this golden path .
This capability is particularly valuable for complex, multi-channel journeys. AI analyzes thousands of customer interactions to identify true intent—distinguishing between “comparing value” versus “checking affordability”—enabling organizations to tailor experiences with unprecedented precision . Journey analytics can highlight which steps disproportionately impact satisfaction or conversion, guiding targeted improvements where they matter most.
Personalization Beyond Plugins: The AI Orchestration Advantage
Modern personalization extends far beyond simply inserting a customer’s name in an email. AI enables true experience orchestration—determining what action, in what channel, at what time, with what tone will drive the desired outcome . This includes:
Next Best Action: Recommending the right support or content at the right step in the journey
Channel Fit: Matching the medium to the message based on individual customer preferences
Predictive Timing: Ensuring outreach happens just before customers disengage, not after
Table: AI-Powered Journey Mapping vs. Traditional Approaches
| Aspect | Traditional Mapping | AI-Powered Mapping |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | Manual, surveys, periodic | Automated, real-time, multi-channel |
| Insight Generation | Human-identified patterns | AI-detected correlations and predictions |
| Personalization | Segment-level | Individual-level |
| Update Frequency | Quarterly/annually | Continuous |
| Proactive Capability | Limited to the hypothesis | Predictive intervention |
Building Intelligent Operations: The Framework for Connected Experiences
Creating truly intelligent customer experiences requires more than technology—it demands a fundamental rewiring of how organizations operate, collaborate, and derive insights. This begins with establishing what we term intelligent operations—operations that harness diverse data driven by applied intelligence and human ingenuity to empower insight-led decision making .
The V-Shaped Team: Breaking Down Silos for Journey Excellence
The first step toward building intelligent operations is assembling what we call V-Shaped teams—cross-functional groups that can communicate effectively across multiple departments regardless of background or skillset. These teams combine deep specialized expertise with broad organizational understanding, enabling them to see customer journeys holistically rather than through functional silos.
The urgency for this cross-functional approach is underscored by research showing that companies with leading digital and AI capabilities outperform lagging competitors by two to six times in terms of total shareholder returns . Despite this, only 28% of organizations are planning to invest in upskilling programs over the next 2-3 years, creating a significant competitive opportunity for those who act decisively .
The Data Foundation: Building Your Customer Intelligence Core
Before AI can work its magic, organizations must establish a robust data foundation. This begins with first-party data strategy that respects customer privacy while delivering value. The most successful organizations focus on three key elements:
Data Fabric Architecture: Providing unified data access across systems, regardless of location
Real-Time Analytics: Enabling immediate response to customer behaviors and needs
Ethical Governance: Establishing clear data consent procedures and guardrails for generative AI
Essential Tools and Technologies for Modern Journey Mapping
Selecting the right technology stack is critical for implementing effective journey mapping in today’s complex digital environment. The ideal toolkit combines visualization capabilities with data integration and analytics functionality.
Journey Mapping Platforms: From Visualization to Activation
Modern journey mapping tools have evolved far beyond simple diagramming software. The most effective platforms now offer:
Real-Time Collaboration: Tools like FigJam enable distributed teams to work simultaneously on journey maps, with built-in templates specifically designed for customer experience mapping
Integration Capabilities: Platforms such as Smaply allow organizations to create journey maps and link them in hierarchies or journey networks, enabling both zoomed-in and zoomed-out views of the customer experience
Analytics Integration: Solutions like Mouseflow automatically track visitor journeys and identify drop-off points, connecting behavior data directly to journey visualization
The Supporting Technology Ecosystem
Journey mapping doesn’t exist in isolation—it requires support from complementary technologies that provide data and enable activation:
Table: Essential Journey Mapping Tool Categories
| Tool Category | Key Function | Example Platforms |
|---|---|---|
| Behavioral Analytics | Track user interactions and identify friction points | Mouseflow, Fullstory |
| Customer Data Platforms | Unify customer data across touchpoints | Totango, CRM systems |
| Collaboration Tools | Enable cross-functional mapping sessions | FigJam, Miro |
| Digital Experience Platforms | Deliver omnichannel experiences | CMS and personalization engines |
The Implementation Blueprint: Creating Actionable Journey Maps
Even with advanced technology, successful journey mapping requires disciplined execution. The following framework ensures your mapping exercises deliver tangible business value.
Phase 1: Foundation and Scope Definition
Begin by defining your map’s scope with precision. Ideally, journey mapping should focus on the experience of a single persona in a single scenario with a single goal. Overly broad scope leads to generic maps that miss critical insights.
Key steps in this phase include:
Persona Development: Create detailed personas informed by actual customer interviews and data
Back-Story Building: Document why your target persona would be on this journey in the first place, including their pain points, requirements, and desired outcomes
Channel Inventory: Identify all touchpoints across websites, mobile apps, physical locations, customer service, and more
Phase 2: Current State Mapping and Pain Point Identification
With scope defined, map the current customer experience through a combination of data analysis and qualitative research:
Touchpoint Sequencing: Plot each action customers take, questions they have, and decisions they make
Sentiment Mapping: Chart emotional highs and lows throughout the journey to identify frustration points and moments of delight
Pain Point Cataloging: Identify specific friction points, noting their impact and frequency
Phase 3: Future State Design and Optimization
Using insights from current state analysis, design improved future experiences:
Moment of Truth Optimization: Focus on touchpoints that disproportionately impact satisfaction or conversion
Channel Alignment: Ensure each touchpoint occurs in the right channel at the right time
Proactive Experience Design: Build in anticipatory elements that address needs before customers articulate them
Measuring Success: Beyond CSAT to Journey-Centric Metrics
Traditional customer satisfaction metrics remain important, but journey-focused measurement requires a more nuanced approach. Organizations should track four key dimensions :
Efficiency: Time-to-resolution, self-service rates, agent productivity
Effectiveness: Progression through steps, conversion rates, yield
Equity and Trust: Opt-in rates, fairness audits, customer complaints
Experience: CSAT/NPS enriched by AI-powered text analysis
The most telling metric is often qualitative: when customers voluntarily comment, “You made this process easier,” you know your systems—and the humans behind them—are working together effectively .
Future-Proofing Your Journey Mapping Practice
As technology continues to evolve, organizations must maintain agile journey mapping practices that adapt to changing customer behaviors and expectations.
The Human-Machine Balance: Maintaining Empathy at Scale
While AI provides unprecedented scaling capabilities, the human element remains irreplaceable for true customer understanding. Organizations must maintain what PwC found: many customers will abandon a brand after a single poor experience—a reminder that human empathy remains a true differentiator.
This balance was exemplified when a global bank implemented a chatbot: while customers appreciated instant answers to common questions, the real breakthrough was designing seamless handoffs to human representatives when complexity or emotion came into play .
Continuous Evolution: Building a Learning System
Customer journeys are never static—they evolve with technology, market conditions, and customer preferences. Organizations must treat journey mapping as a continuous practice rather than a periodic project. This includes:
Regular Journey Reviews: Establish quarterly journey assessment cycles to identify changes and opportunities
Test-and-Learn Culture: Implement pilot programs to test journey improvements before full-scale deployment
Cross-Functional Journey Governance: Assign journey owners responsible for specific experience segments
Conclusion: Mapping the Future of Customer Experience
The organizations that will thrive in the coming years are those that recognize customer journey mapping not as a UX exercise but as a fundamental business discipline. By combining AI’s pattern recognition capabilities with human empathy and strategic thinking, companies can move beyond reactive problem-solving to anticipatory experience design.
The future of customer journey mapping lies in creating dynamic, self-updating systems that not only reflect current customer behaviors but also predict future needs and preferences. This requires investment in both technology and talent—particularly in developing V-shaped employees who can bridge functional silos and translate data insights into human-centered experiences.
As you embark on your journey mapping evolution, remember that the goal is not to create perfect maps but to foster perfect understanding—the kind that enables you to meet customers where they are, anticipate where they’re going, and design experiences that feel less like transactions and more like relationships.
For further exploration of the specific tools mentioned, visit these resources:
FigJam: https://www.figma.com/figjam/
Mouseflow: https://mouseflow.com/
Smaply: https://www.smaply.com/
Comprehensive digital transformation trends: https://www.prosci.com/blog/digital-transformation-trends-in-2025-and-beyond