A Comprehensive Guide to Agile Design
In the ever-evolving world of product design and development, agility and adaptability have become indispensable.
Lean UX, a methodology rooted in these principles, has emerged as a transformative approach to creating user-centric products efficiently.
By focusing on collaboration, rapid experimentation, and iterative processes, Lean UX addresses the dynamic needs of modern businesses and users alike.
In this post, we delve deep into what it is, its benefits, best practices, and how it stands out in the realm of product design.
Understanding Lean UX
Lean UX is a design methodology that prioritizes creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) and iterating on it based on user feedback.
Unlike traditional UX design processes, which often emphasize comprehensive upfront design specifications, Lean UX focuses on delivering value swiftly by validating assumptions and adapting to insights gathered through real-world user interaction.
Origins of Lean UX
The methodology draws its core principles from the Lean Startup methodology, which advocates for:
- Building and testing MVPs to validate assumptions.
- Minimizing waste in product development.
- Embracing an iterative approach to deliver value faster.
By integrating these principles, the methodology enables teams to:
- Rapidly identify what works and what doesn’t.
- Make timely adjustments based on real user feedback.
- Align design decisions with both user needs and business goals.
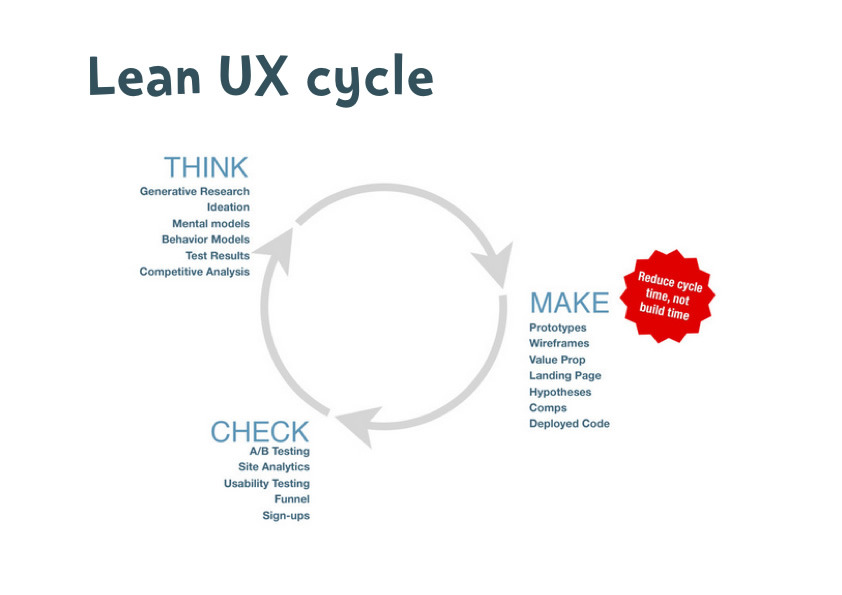
The Lean UX Process
The methodology process is iterative, collaborative, and focused on outcomes. Here’s a breakdown of its key steps:
1. Define the Problem
Every successful design begins with a clear understanding of the problem. In Lean UX, this involves:
- Conducting market research to understand industry trends.
- Performing user interviews to gather direct insights.
- Identifying pain points and opportunities through customer journey mapping.
The goal is to frame a problem statement that guides the design process.
2. Ideate
Once the problem is defined, the next step is to generate ideas for potential solutions. This stage often includes:
- Brainstorming sessions with cross-functional teams.
- Sketching concepts to visualize ideas.
- Utilizing techniques like Crazy 8s or storyboarding to explore diverse perspectives.
3. Prototype
Prototyping in Lean UX is about creating quick, tangible representations of ideas. These can range from:
- Paper prototypes for low-fidelity testing.
- Digital mockups using tools like Figma or Sketch.
- Interactive prototypes to simulate user interactions.
The objective is to test hypotheses without over-investing time and resources.
4. Test
Testing prototypes with real users is a cornerstone of the methodology . Methods include:
- Usability testing to observe how users interact with the product.
- Conducting focus groups to gather qualitative insights.
- Gathering quantitative data through A/B testing or analytics tools.
Feedback from this phase directly informs the next iteration.
5. Iterate
The methodology thrives on continuous improvement. Designers refine their solutions based on user feedback, repeating the prototype-test-iterate cycle until the product aligns with user needs and business goals.
6. Launch
When a product meets the desired criteria, it’s ready for launch. However, even after deployment, Lean UX emphasizes ongoing testing and updates to adapt to evolving user needs.
Key Principles of Lean UX
1. Collaboration
The methodology breaks down silos by encouraging designers, developers, and stakeholders to work closely together. This fosters a shared understanding of goals and ensures alignment across teams.
2. User-Centric Design
By prioritizing user needs, Lean UX ensures that products are not only functional but also resonate with the target audience.
3. Rapid Experimentation
Quickly testing ideas reduces the risk of investing heavily in unvalidated solutions. This approach emphasizes learning through doing.
4. Outcome Over Output
Lean UX measures success by outcomes—improved user satisfaction, engagement, or business metrics—rather than the volume of deliverables produced.
Benefits of Lean UX
1. Faster Time to Market
By focusing on MVPs and iterative design, the methodology accelerates the development process, enabling teams to respond swiftly to market demands.
2. Cost Efficiency
Avoiding lengthy design cycles and minimizing waste saves resources, making Lean UX a cost-effective approach.
3. Enhanced Collaboration
Cross-functional teamwork leads to cohesive solutions and fosters a sense of shared ownership among team members.
4. Improved User Experience
Continuous user testing ensures that design decisions are informed by real user needs, leading to products that delight and engage users.
5. Increased Customer Satisfaction
By iterating based on feedback, Lean UX helps create products that align closely with customer expectations and preferences.
Best Practices for Lean UX in Product Development
To maximize the effectiveness of Lean UX, consider these best practices:
1. Adopt Rapid Prototyping
Utilize tools like:
- Figma
- Adobe XD
- InVision
These platforms allow for quick creation and testing of prototypes, enabling faster iterations.
2. Prioritize User Testing
Make user feedback a constant in your design process. Techniques like usability testing, surveys, and heatmaps provide actionable insights.
3. Embrace Iterative Design
Work in short, focused sprints. Each cycle should:
- Introduce small changes.
- Test their impact.
- Refine the product accordingly.
4. Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration
Bring together designers, developers, product managers, and stakeholders to ensure alignment and encourage diverse perspectives.
5. Measure Outcomes
Define and track metrics such as:
- Customer retention rates
- Task completion times
- Conversion rates
These provide a clear picture of the product’s success.
Common Challenges in Lean UX
1. Balancing Speed and Quality
Rapid iteration can sometimes lead to overlooked details. Establishing clear quality benchmarks can mitigate this risk.
2. Stakeholder Buy-In
Educating stakeholders on the iterative nature of Lean UX and its long-term benefits is essential for smooth implementation.
3. Integration with Agile Development
Aligning Lean UX with Agile workflows requires clear communication and shared processes to avoid misalignment.
Conclusion
Lean UX represents a shift from traditional design paradigms to a more agile, user-focused approach. By emphasizing collaboration, iterative processes, and rapid experimentation, Lean UX empowers teams to create impactful products that resonate with users and achieve business goals.
Whether you’re a startup navigating uncertain markets or an established company seeking to innovate, Lean UX offers a proven methodology to stay ahead. By integrating its principles and practices into your workflow, you can unlock the potential for faster, more efficient, and user-centric product development.
For further reading on Lean UX, consider exploring these resources:
- The Lean Startup by Eric Ries
- Lean UX: Applying Lean Principles to Improve User Experience
- Agile UX and Lean UX Practices
Embrace Lean UX, and transform the way you design for today’s fast-paced, ever-changing world.
If you want to learn more about this topic, you should visit shopify.com website (LINK)
Image belongs to We Love Lean (LINK)