Affect Grid in UX Design
Introduction
In the evolving landscape of user experience (UX) design, understanding user emotions has become as critical as crafting visually appealing and functional interfaces.
Among the tools that UX designers can employ to map and interpret user emotions, the Affect Grid stands out as a robust framework.
This tool helps designers analyze and predict how users feel about a product or service, ensuring emotional resonance and an optimized user journey.
This blog will delve deep into what the Affect Grid is, how it works, and its transformative potential in UX design.
What is the Affect Grid?
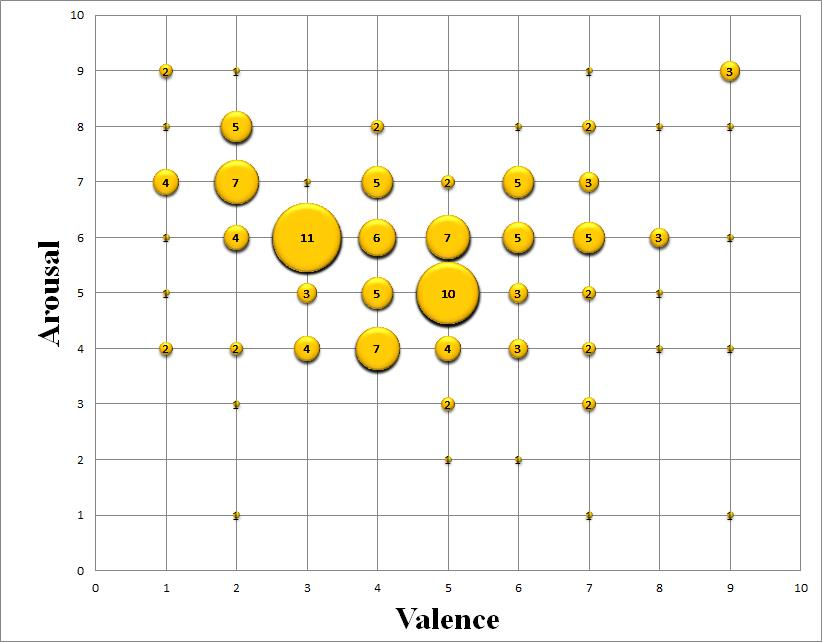
The Affect Grid is a two-dimensional framework designed to map human emotions. Rooted in the principles of affective computing – the study of how systems can recognize, interpret, and simulate human emotions – this tool aids UX designers in assessing user emotions systematically.
The grid comprises two axes:
- Y-axis (Arousal): Measures the intensity of emotions, ranging from low (calm, subdued) to high (excited, intense).
- X-axis (Valence): Indicates the polarity of emotions, from negative (unpleasant) to positive (pleasant).
Each coordinate on this grid represents a unique emotional state, providing a visual representation of user feelings during an interaction with a product or service.
Key Concepts
- Intensity (Arousal): Refers to how strongly or weakly an emotion is felt.
- Valence: Determines whether the emotion is positive or negative.
How Does the Affect Grid Work?
The Affect Grid operates by plotting emotional responses based on user input. This input can come from textual data, verbal feedback, or behavioral cues. Using natural language processing (NLP) and emotion detection algorithms, the tool interprets emotional data and visualizes it on the grid. For instance:
- A high-arousal, positive-valence point could represent excitement or joy.
- A low-arousal, negative-valence point might signify boredom or disappointment.
This mapping enables designers to:
- Identify emotional highs and lows in the user experience.
- Pinpoint areas needing improvement to elevate user satisfaction.
Benefits of Using the Affect Grid in UX Design
1. Data-Driven Emotional Insights
By leveraging the Affect Grid, UX designers move beyond guesswork. The tool provides tangible data on user emotions, making it easier to:
- Predict emotional responses to new features.
- Tailor designs to foster positive user experiences.
For instance, analyzing user feedback about a mobile app’s navigation can reveal whether users find it intuitive and engaging or frustrating and complex.
2. Enhanced Collaboration Across Teams
The tool offers a standardized framework for emotional analysis. In large organizations where multiple teams contribute to the same product, this consistency facilitates better collaboration. Everyone—from designers to marketers—works from a shared understanding of user emotions.
3. Improved User Retention and Loyalty
Emotional resonance often determines whether users return to a product or abandon it. By identifying pain points and optimizing pleasurable experiences, the Affect Grid helps in:
- Boosting user retention.
- Building emotional connections that foster loyalty.
Key Highlights of the Affect Grid
Origins in Emotional Psychology
The Affect Grid is inspired by the Plutchik Emotion Wheel, a model developed by psychologist Robert Plutchik in the 1980s. This wheel categorizes emotions into primary pairs (e.g., joy-sadness, anger-fear) and forms the basis for understanding emotional combinations.
Versatility of Applications
The Affect Grid’s 9×9 structure accommodates nuanced emotional states. Designers can:
- Analyze social media sentiment.
- Assess customer feedback for emotional tone.
- Evaluate user interactions with a digital interface.
For example, a low-arousal, positive-valence emotion might reflect satisfaction, while high-arousal, negative-valence could indicate frustration.
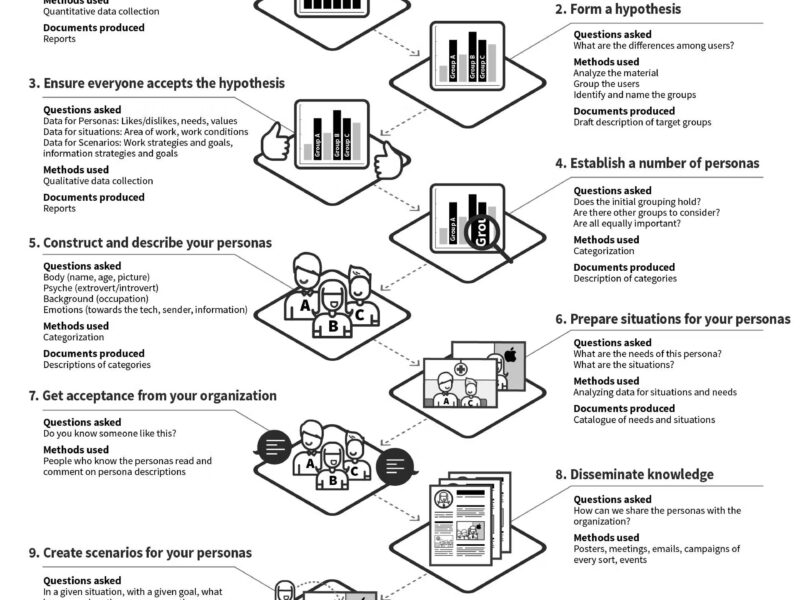
Steps to Implement the Affect Grid in UX Research
Step 1: Define Objectives
Determine what you aim to achieve by using the Affect Grid. Are you analyzing emotional feedback for a new feature or studying how users feel about your product’s overall design?
Step 2: Collect Data
Gather textual or behavioral data from users. Common sources include:
- Social media posts.
- Customer reviews.
- Survey responses.
- Focus group transcripts.
Step 3: Input Data into the Tool
Use tools equipped with NLP to process the collected data to generate a visualization of the emotional distribution.
Step 4: Analyze Results
Examine the grid to understand key emotional trends:
- Identify dominant emotions.
- Assess overall sentiment (positive, negative, neutral).
- Evaluate the intensity of emotional responses.
Step 5: Inform Design Decisions
Translate your findings into actionable design changes. For instance:
- Address areas causing high-arousal, negative-valence emotions.
- Amplify features that evoke high-arousal, positive-valence responses.
Step 6: Iterate and Test
Continuous improvement is key. Test the updated designs with users and analyze new data to refine the emotional experience.
Practical Use Cases
1. Customer Feedback Analysis
An e-commerce platform might use the Affect Grid to analyze reviews. If many users express high-arousal, negative-valence emotions about checkout complexity, designers can streamline the process.
2. Content Sentiment Analysis
For content-heavy platforms, such as blogs or social media apps, the Affect Grid can help identify content that resonates positively with users.
3. Feature Testing
When launching a new feature, the Affect Grid enables designers to gauge initial emotional responses and refine the feature accordingly.
Tools and Technologies
Several tools integrate Affect Grid principles:
- IBM Watson Tone Analyzer
- Provides sentiment and emotion analysis.
- URL: IBM Watson
- Affectiva’s Emotion AI
- Specializes in detecting emotions through facial expressions and tone of voice.
- URL: Affectiva
- Microsoft Text Analytics
- Offers sentiment analysis and key phrase extraction.
- URL: Microsoft Azure AI
Conclusion
The Affect Grid is more than just a theoretical framework; it’s a practical tool that empowers UX designers to create emotionally resonant experiences.
By mapping user emotions and leveraging these insights, designers can craft products that not only meet functional needs but also resonate emotionally with their users.
In a world where user experience can make or break a product, understanding and optimizing emotional connections is no longer optional—it’s essential.
Start integrating the Affect Grid into your UX processes today and witness the transformative impact on your designs.
Further Reading
- The Role of Emotions in UX Design – NNGroup
- Plutchik’s Wheel of Emotions – Verywell Mind
- Affective Computing and Its Role in UX – Interaction Design Foundation
I you’re interested in Affect Grid here’s the link to the paper “Stress in interactive applications: analysis of the valence-arousal space based on physiological signals and self-reported data“