What is a UX Design Factory?
A UX Design Factory is a specialized organization dedicated to crafting exceptional user experiences (UX) for digital products such as websites, mobile applications, and software solutions.
Its primary objective is to help businesses create digital products that are intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable for their target audience.
The UX Design Process
The journey to delivering an iconic user experience involves several key stages:
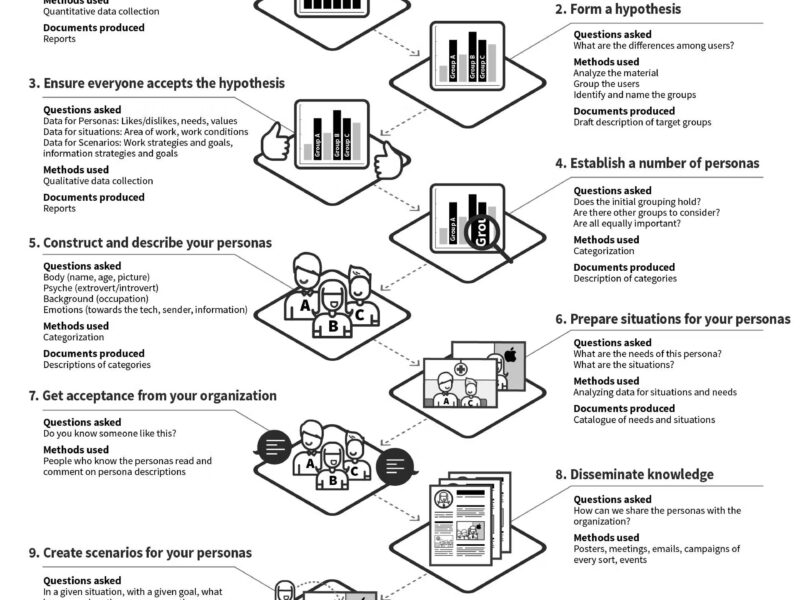
- User Research: Understanding the target audience through interviews, surveys, and usability testing to uncover pain points and opportunities for improvement.
- Design: Creating wireframes, mockups, and prototypes, followed by rigorous user testing to validate usability and effectiveness.
- Development & Implementation: Collaborating with developers to ensure accurate translation of designs into functional products, including comprehensive testing and quality assurance.
- Ongoing Support: Offering continuous user research, data analysis, and updates to maintain relevance and effectiveness.
Services Offered by a UX Design Factory
A UX Design Factory provides a range of services, including:
- User Research: Identifying audience needs and pain points through surveys, usability testing, and data analysis.
- Design: Developing wireframes, prototypes, and high-fidelity mockups, ensuring alignment with user needs.
- Accessibility: Creating inclusive designs compliant with accessibility standards.
- Optimization: Using data-driven insights to enhance usability and engagement.
- Internationalization: Adapting products for different languages and cultures to ensure global resonance.
- Consultancy: Providing expert advice to refine existing designs or guide new developments.
Governance Model of a UX Design Factory
A robust governance model ensures efficient operations:
- Organizational Structure: Clearly defined roles, such as designers, researchers, and developers.
- Decision-Making: Transparent processes for resolving conflicts and making critical decisions.
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring products meet user expectations through testing and research.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Incorporating client and user feedback for continuous improvement.
Roles Within a UX Design Factory
Each role contributes uniquely to the success of the factory:
- UX Designer: Creates user-friendly wireframes and prototypes.
- UI Designer: Focuses on aesthetics and brand alignment.
- UX Researcher: Conducts research to inform design decisions.
- Interaction Designer: Develops intuitive interactive elements.
- Information Architect: Organizes content for seamless navigation.
- Accessibility Specialist: Ensures inclusivity for all users.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Success
Measuring success involves tracking:
- User Satisfaction: Through surveys and feedback.
- Conversion Rates: Monitoring desired user actions.
- Task Completion Rates: Evaluating usability.
- Bounce Rates: Analyzing user engagement.
Agile Methodology in a UX Design Factory
Agile principles enhance efficiency and collaboration. Steps include:
- Cross-Functional Teams: Integrating designers, developers, and researchers.
- Sprint Planning: Defining goals and deliverables.
- User-Centered Design: Involving users in every design stage.
- Continuous Improvement: Iterating based on feedback.
Essential Tools for Success
- Research Tools: UserTesting, Optimal Workshop.
- Design Tools: Figma, Adobe XD.
- Project Management: Jira, Trello.
- Collaboration: Slack, Zoom.
- Accessibility: WAVE, Accessibility Insights.
Conclusion
A UX Design Factory is central to creating impactful digital products that resonate with users. By integrating structured processes, leveraging essential tools, and fostering collaboration, businesses can achieve enhanced user satisfaction and long-term success.
Whether you’re launching a new product or refining an existing one, embracing these principles ensures innovation and growth in the digital era.
References
- Nielsen Norman Group: https://www.nngroup.com
- Interaction Design Foundation: https://www.interaction-design.org
- UX Collective: https://uxdesign.cc