In today’s digital landscape, usability and UX design process are critical for creating products that resonate with users.
A structured UX design process ensures efficiency, aligns stakeholder goals, and minimizes costly redesigns.
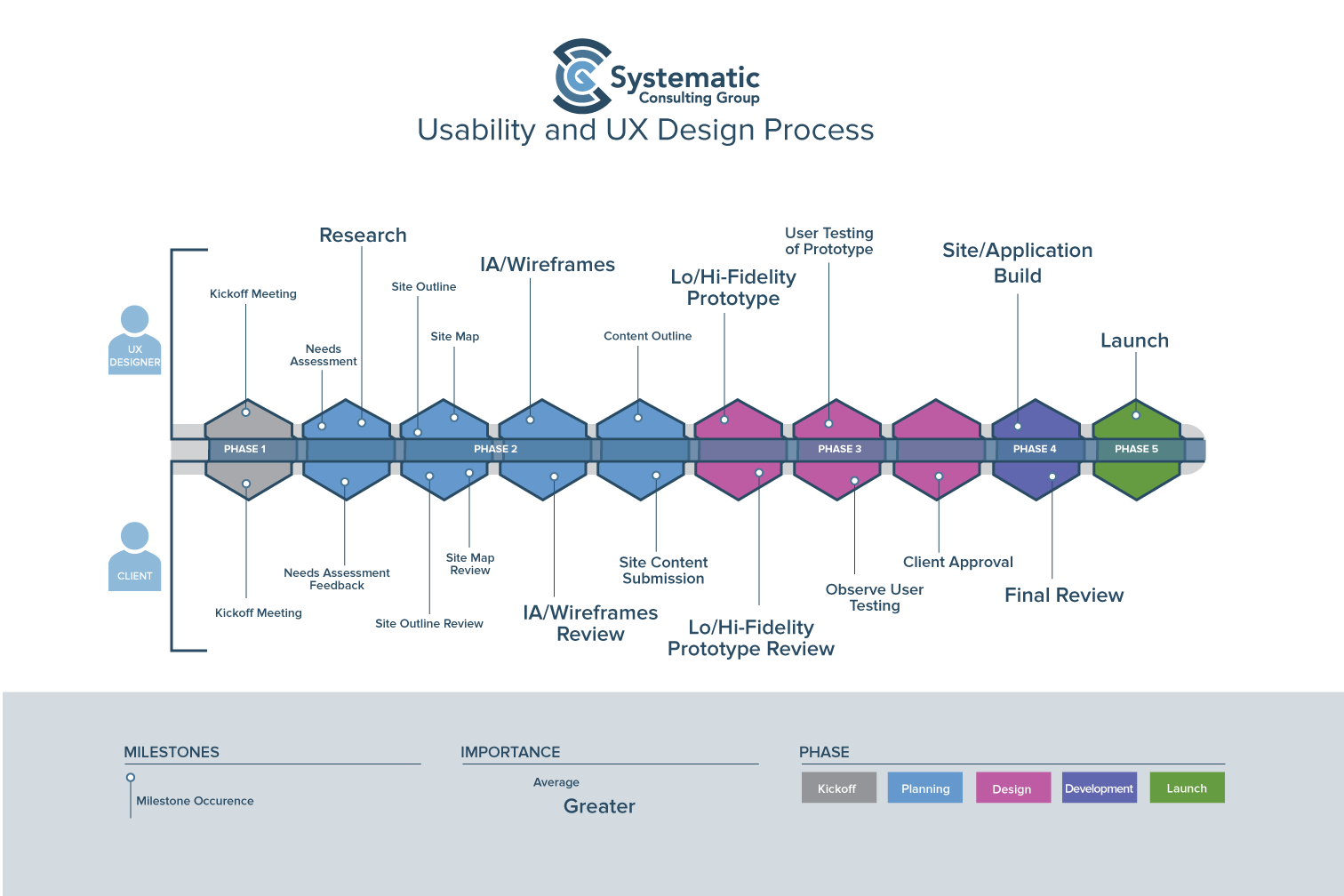
Drawing from Systematic Consulting Group’s proven methodology—including phases like PENGINE (Project Engine) and CLEVIT (Client Evolution Integration)—this guide explores the end-to-end process of crafting user-centric designs.
The Importance of a Structured UX Design Process
A systematic approach to UX design bridges gaps between user needs, business objectives, and technical feasibility. Studies show that every 1 invested in UX yields 100 in return (Forrester, 2016). Structured processes like PENGINE ensure:
- Consistency across teams.
- Clear milestones (e.g., Kickoff, Prototype Review).
- Reduced risk of post-launch failures.
Understanding UX Design
What is UX Design?
User Experience (UX) design is the process of enhancing user satisfaction by improving usability, accessibility, and interaction between the user and the product. It involves research, design, prototyping, and testing to create seamless and enjoyable experiences.
Why is UX Important?
- Enhances User Satisfaction – A well-designed UX makes interactions intuitive and enjoyable.
- Improves Engagement – Good usability keeps users engaged, reducing bounce rates.
- Increases Conversions – UX-optimized products drive higher conversion rates.
- Reduces Costs – Addressing usability issues early prevents expensive redesigns later.
The UX Design Process
The UX design process is iterative and consists of several key phases:
Phase 1: Research
Before designing a product, thorough research is required to understand user needs, business objectives, and market trends.
1.1 User Research
- Conduct surveys, interviews, and usability testing.
- Analyze user behavior through data analytics.
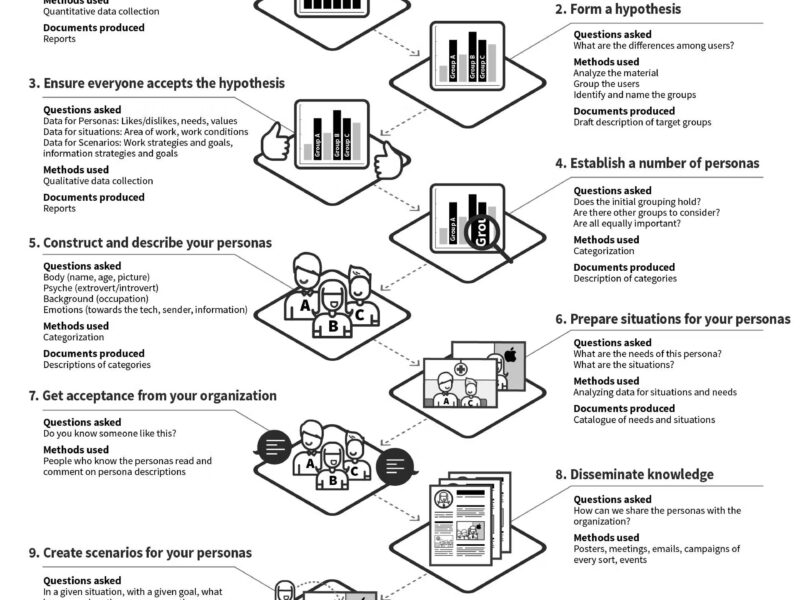
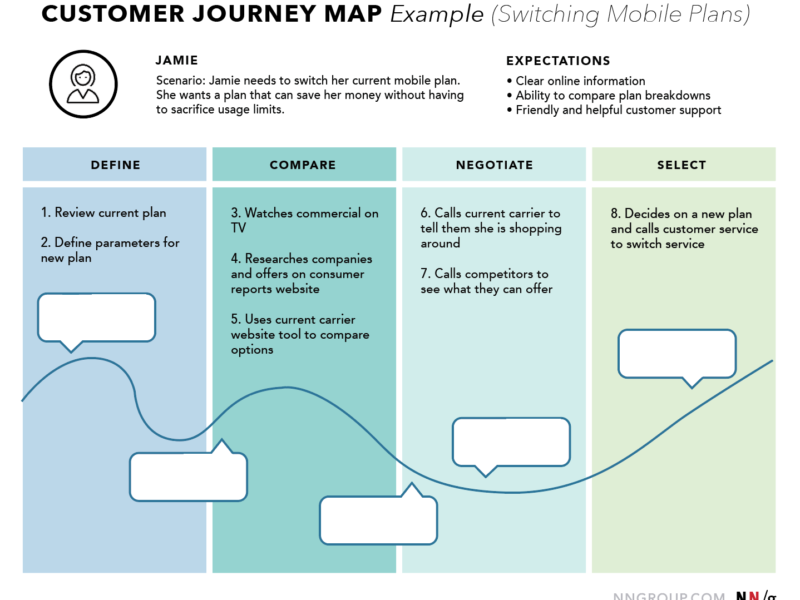
- Create user personas and journey maps.
1.2 Competitive Analysis
- Evaluate competitors’ UX strategies.
- Identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities.
1.3 Define Objectives
- Set measurable usability and UX goals.
- Align user needs with business objectives.
Phase 2: Information Architecture (IA) & Wireframing
This phase structures content and defines the layout of the product.
2.1 Information Architecture (IA)
- Organize content logically.
- Use card sorting and tree testing.
- Develop sitemaps and navigation structures.
2.2 Wireframing & Prototyping
- Create low-fidelity wireframes to outline structure.
- Develop interactive prototypes for testing.
- Iterate based on feedback.
Phase 3: UI Design & Prototyping
This phase focuses on visual and interactive elements.
3.1 Visual Design
- Implement branding elements (colors, typography, icons).
- Ensure accessibility compliance (WCAG standards).
3.2 High-Fidelity Prototypes
- Use tools like Figma, Adobe XD, or Sketch.
- Simulate real-world interactions.
Phase 4: User Testing & Iteration
Testing is essential to identify usability issues and improve the design.
4.1 Usability Testing
- Conduct A/B testing and heatmap analysis.
- Gather user feedback through moderated sessions.
4.2 Iterate and Improve
- Make data-driven design refinements.
- Continue usability testing until optimal performance is achieved.
Phase 5: Development & Implementation
Once the design is finalized, the development team builds the product.
5.1 Collaboration with Developers
- Ensure smooth handoff through design documentation.
- Use component-based design systems.
5.2 Quality Assurance & Testing
- Perform accessibility and cross-device testing.
- Fix usability issues before deployment.
Phase 6: Launch & Continuous Optimization
After deployment, ongoing monitoring and improvements are necessary.
6.1 Post-Launch Analysis
- Track usability metrics (bounce rates, session duration, etc.).
- Gather real-world user feedback.
6.2 UX Optimization
- Implement enhancements based on analytics.
- Keep the design adaptive to user needs.
Best Practices for Usability and UX Design
- Adopt a User-Centered Design Approach – Prioritize user needs at every stage.
- Maintain Consistency – Use uniform UI elements for familiarity.
- Ensure Accessibility – Follow WCAG guidelines for inclusivity.
- Simplify Navigation – Make user flows intuitive.
- Test Early & Often – Regular testing prevents costly errors.
Conclusion
The UX design process is essential for creating user-friendly, effective digital experiences. By following structured methodologies, leveraging research, and continuously improving based on feedback, businesses can enhance user satisfaction and drive success.
For further insights, check out resources from NNGroup and Smashing Magazine.