Design Thinking and Strategic Innovation
Design Thinking is more than a buzzword—it’s a human-centered approach to solving complex problems and unlocking strategic innovation.
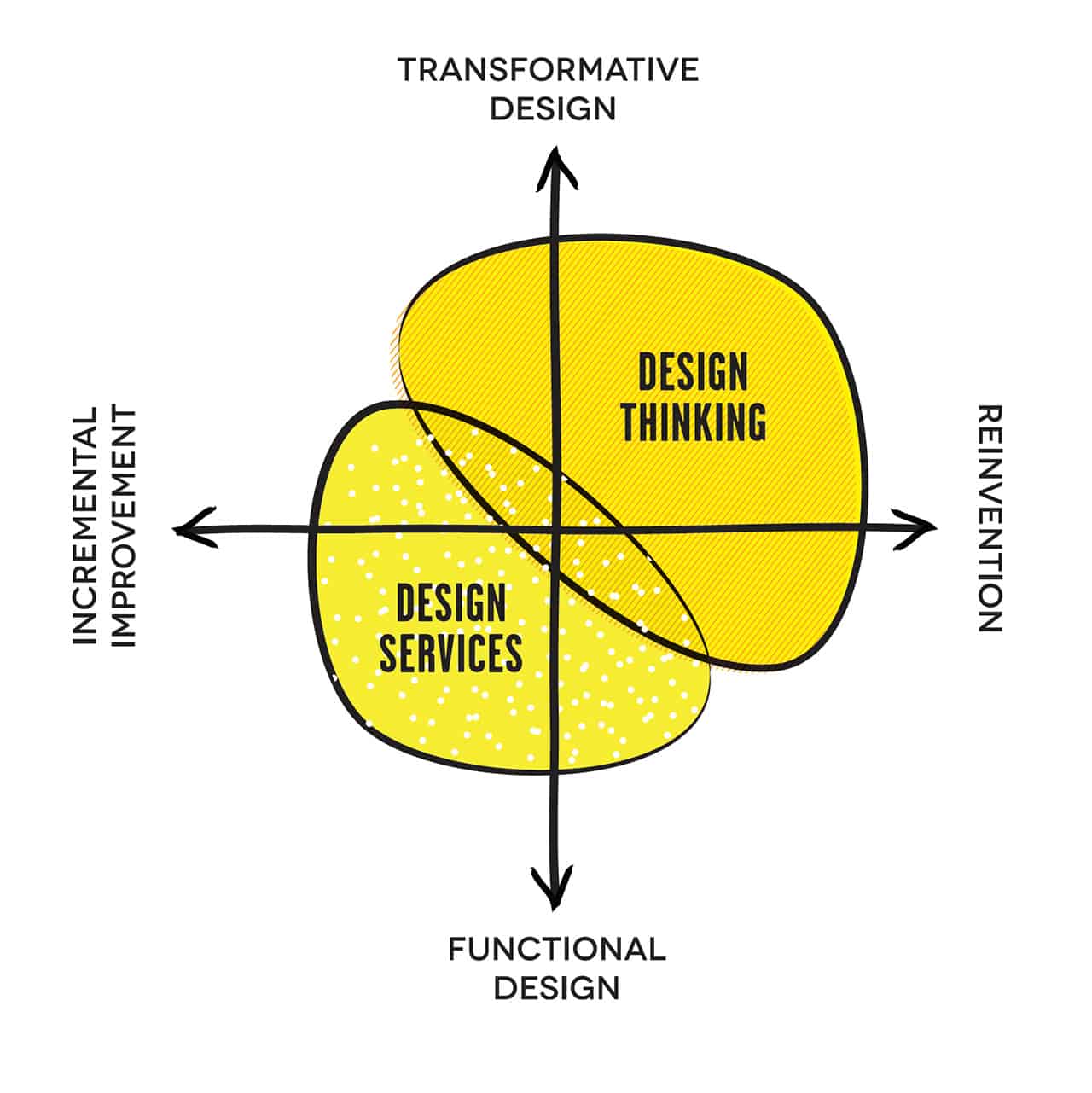
By blending empathy, creativity, and iterative learning, organizations can pivot from stagnation to disruption. This post unpacks how Design Thinking intersects with four pillars of innovation: Transformative Design, Incremental Improvement, Functional Design, and Resign Reinvention.
According to IDEO, a global leader in Design Thinking, this methodology “tackles ill-defined or unknown problems by reframing them in human-centric ways” (IDEO, What is Design Thinking?). When applied strategically, it becomes a catalyst for reimagining industries, products, and user experiences.
The Pillars of Strategic Design Innovation
1. Transformative Design: Redefining Industries
Transformative Design disrupts markets by addressing unmet needs through radical innovation. Think of Apple’s iPhone, which redefined mobile communication, or Tesla’s electric vehicles, which challenged automotive norms. These breakthroughs stem from empathy-driven insights and a willingness to question the status quo.
Key strategies:
- Human-Centered Research: Conduct ethnographic studies to uncover latent user needs.
- Prototyping Bold Ideas: Test concepts early, as Airbnb did with its initial home-sharing model (Harvard Business Review, The Power of Prototyping).
2. Incremental Improvement: Sustaining Competitive Edge
Not all innovation requires reinvention. Incremental Improvement focuses on refining existing products or services. Amazon’s relentless UI optimizations—like one-click ordering—exemplify how small tweaks drive loyalty and efficiency.
Tools for success:
- A/B Testing: Validate changes using platforms like Optimizely.
- Feedback Loops: Leverage tools like Hotjar to analyze user behavior (Nielsen Norman Group, Continuous UX Improvement).
3. Functional Design: Balancing Aesthetics and Usability
Functional Design prioritizes usability without sacrificing aesthetics. Slack’s intuitive interface or Zoom’s seamless meeting controls demonstrate how form and function coexist. As Don Norman, author of The Design of Everyday Things, states: “Good design makes a product understandable” (Don Norman, The Design of Everyday Things).
Best practices:
- User Journey Mapping: Visualize pain points with tools like Miro.
- Accessibility Compliance: Follow WCAG guidelines to ensure inclusivity.
4. Resign Reinvention: Letting Go to Move Forward
Resign Reinvention involves abandoning outdated models to embrace new paradigms. Nintendo’s shift from hardware (e.g., Wii) to software (e.g., Animal Crossing: New Horizons) illustrates this. It requires courage to “kill your darlings” and pivot strategically.
Steps to execute:
- Scenario Planning: Anticipate market shifts using frameworks from McKinsey (McKinsey, Strategic Resilience).
- Agile Leadership: Foster a culture that embraces change, as Satya Nadella did at Microsoft.
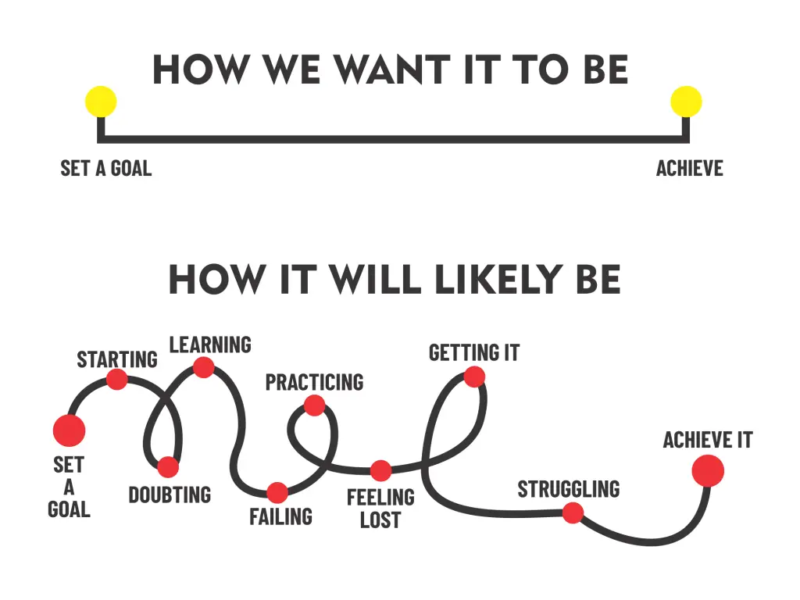
The Design Thinking Process: From Empathy to Implementation
Design Thinking follows five stages, as defined by the Stanford d.school:
- Empathize: Understand user needs through interviews and surveys.
- Define: Synthesize insights into problem statements.
- Ideate: Brainstorm solutions with cross-functional teams.
- Prototype: Build low-fidelity models for testing.
- Test: Iterate based on feedback.
For example, IBM’s Enterprise Design Thinking framework has driven a 301% ROI for clients by aligning teams around user outcomes (IBM, The Value of Design Thinking).
Case Studies: Design Thinking in Action
- PillPack (Amazon Pharmacy): By focusing on elderly users’ medication management struggles, PillPack simplified prescription delivery, leading to Amazon’s $1B acquisition (Fast Company, PillPack Case Study).
- IDEO and Bank of America’s Keep the Change Program: A rounding-up savings feature born from observing customers’ financial habits (IDEO Case Study).
Tools and Methodologies
- Empathy Maps: Visualize user emotions with templates from Xtensio (Xtensio Empathy Map).
- Service Blueprints: Map end-to-end experiences using Lucidchart.
- Design Sprints: Google Ventures’ 5-day framework accelerates innovation (GV Design Sprint).
Overcoming Challenges in Design Thinking
Common obstacles include stakeholder resistance and siloed teams. To mitigate:
- Educate Leadership: Share success stories like PepsiCo’s design-driven growth under Mauro Porcini (Harvard Business Review, Design-Led Strategy).
- Cross-Department Collaboration: Use tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams to bridge gaps.
The Future of Design Thinking
Emerging trends like AI-driven prototyping (e.g., Figma’s AI tools) and ethical design frameworks will shape the next decade. As IBM notes, “Design Thinking is the glue that connects emerging tech to human needs” (IBM, Future of Design).
Conclusion
Design Thinking isn’t a one-time project—it’s a mindset for perpetual innovation. Start small: conduct a user interview, sketch a prototype, or challenge a legacy process. For deeper learning, explore courses on Coursera (IDEO U) or Nielsen Norman Group’s UX certifications.
One thought on “Design Thinking for Strategic Innovation”