User Experience (UX) Design focuses on creating digital products that deliver positive and engaging user experiences.
It involves designing websites, software applications, and other digital interfaces to be intuitive, user-friendly, and effective.
Seasoned UX designers rely on a variety of tools and techniques while adhering to best practices that ensure the success of their designs.
In this blog post, we’ll explore foundational UX design best practices that every designer should consider when crafting exceptional user experiences.
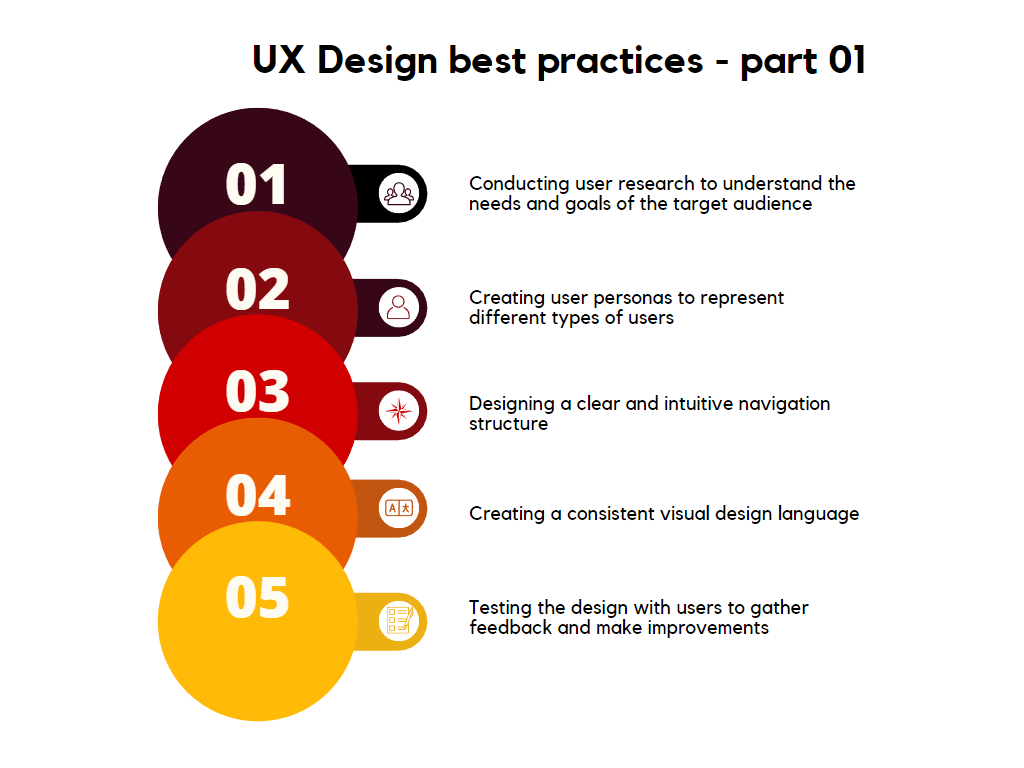
1. Conducting User Research to Understand the Target Audience
Understanding the needs, goals, and pain points of the target audience is the cornerstone of effective UX design. User research helps designers create products tailored to real users, ensuring the interface aligns with their expectations.
Methods for Conducting User Research
- Interviews: One-on-one conversations to gather in-depth insights about users’ needs and behaviors.
- Surveys: Broader outreach to collect quantitative and qualitative data from a larger audience.
- Usability Testing: Observing users interact with a product to identify usability issues.
- Contextual Inquiry: Studying users in their natural environments to understand how they engage with a product.
- A/B Testing: Comparing two versions of a design to determine which performs better.
Benefits of User Research
- Identifies user demographics, behaviors, needs, and pain points.
- Validates assumptions and uncovers new opportunities.
- Informs decisions on features, functionality, and overall user experience.
Pro Tip: User research is an ongoing process. Revisit it regularly to adapt to changing user needs and behaviors.
2. Creating User Personas to Represent Different User Types
User personas are fictional characters based on real user research, representing different user types. They help designers empathize with the target audience and make decisions aligned with users’ needs.
Key Elements of User Personas
- Name and Photo: Personalize the persona to make it relatable. Tools like This Person Does Not Exist can help generate realistic images.
- Demographics: Age, gender, occupation, education level, and income.
- Behavioral Traits: Goals, motivations, habits, and pain points.
- Technical Proficiency: Device preferences and familiarity with technology.
- Attitudes and Values: Broader beliefs that influence decision-making.
How Personas Improve UX Design
- Clarify the needs of diverse user groups.
- Guide the creation of scenarios and user stories.
- Prevent designs from catering to a generic or non-existent “average” user.
Important Note: Personas should evolve with ongoing research and should never stereotype users.
3. Designing a Clear and Intuitive Navigation Structure
A well-structured navigation system ensures users can quickly and easily find what they’re looking for. It’s a critical component of user satisfaction and overall usability.
Best Practices for Navigation Design
- Keep it Simple: Minimize the number of clicks required to access information.
- Use Clear Labels: Ensure menu items and links are descriptive and unambiguous.
- Leverage Familiar Patterns: Follow established conventions, such as a top navigation bar or hamburger menu for mobile.
- Establish a Visual Hierarchy: Highlight key items while grouping related content logically.
- Test with Users: Validate your navigation design through user testing.
Considerations for Mobile Navigation
Given the prevalence of mobile browsing, designers should:
- Use responsive design principles.
- Optimize for smaller screens and touch interactions.
- Ensure navigation elements are easily accessible with one hand.
4. Establishing a Consistent Visual Design Language
A consistent visual design language ensures cohesion across the interface, fostering trust and familiarity. It’s essential for building a strong brand identity and improving user comprehension.
Components of a Visual Design Language
- Color Palette: Define primary, secondary, and accent colors for consistent usage.
- Typography: Standardize font families, sizes, and styles.
- Icons and Imagery: Maintain uniform design styles for graphical elements.
- Layouts: Use consistent grids, spacing, and alignment.
Benefits of Consistency
- Enhances usability by reducing cognitive load.
- Strengthens brand recognition.
- Creates a polished, professional appearance.
Actionable Tip: Regularly review your design language to ensure consistency and refine as needed.
5. Testing Designs with Users to Gather Feedback
User testing provides invaluable insights into how real users interact with a design, helping identify issues and areas for improvement.
Methods of User Testing
- Usability Testing: Have users complete tasks while observing their behavior.
- Surveys: Collect feedback on user satisfaction and perceived usability.
- Interviews: Dive deeper into users’ thoughts and experiences.
Best Practices for Effective Testing
- Set Clear Goals: Define what you want to learn from the testing process.
- Recruit Relevant Participants: Choose users who represent your target audience.
- Plan Scenarios: Design tasks that reflect real-world usage.
- Analyze Results: Identify trends and actionable insights.
- Iterate: Make improvements and test again to validate changes.
Why Testing Matters
Testing not only improves usability but also validates that the design meets user needs. It’s a vital step in creating a product that truly resonates with its audience.
Conclusion: Putting UX Best Practices Into Action
Adhering to these best practices lays the groundwork for successful UX design:
- Conduct thorough user research.
- Develop detailed user personas.
- Prioritize clear and intuitive navigation.
- Maintain a consistent visual design language.
- Test with users and iterate based on feedback.
By embracing these principles, designers can craft digital products that are both functional and delightful, ensuring a positive user experience.
References
- Nielsen Norman Group. (n.d.). User Research Methods
- Interaction Design Foundation. (n.d.). Personas
- Smashing Magazine. (n.d.). Effective Navigation Design
- Adobe. (n.d.). Visual Design Best Practices
- Usability.gov. (n.d.). Usability Testing
Optimize your design processes with these insights, and remember that UX is a journey, not a destination.
If you want to continue learning about this topic, you should visit the below links: