A Human-Focused Approach to Application Development
In the fast-paced world of technology, creating successful applications requires more than just technical prowess. It demands a deep understanding of user needs, behaviors, and motivations.
This is where 7D Product Design comes in—a human-focused approach that emphasizes empathy, collaboration, and iterative development.
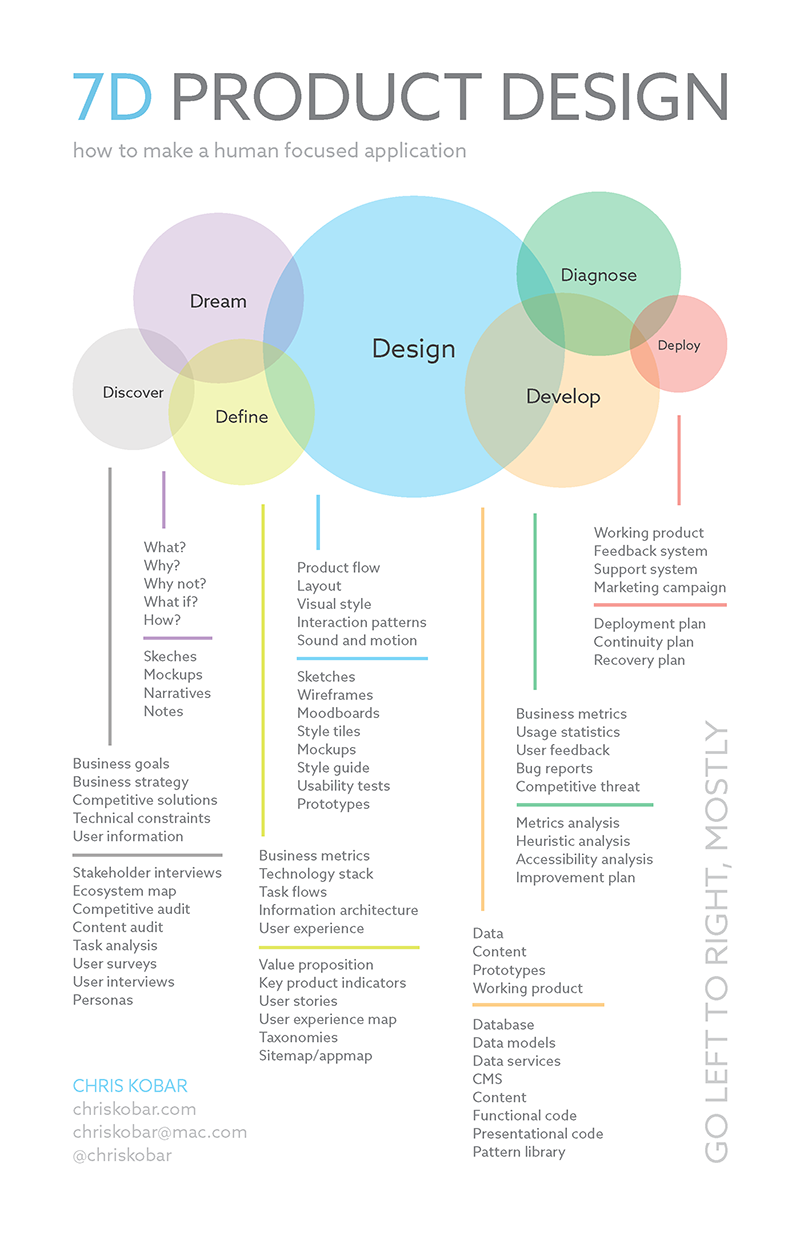
What is 7D Product Design?
7D Product Design is a comprehensive framework that guides the creation of user-centered applications. It encompasses seven key phases, each represented by a “D” word:
- Discover: Understanding the problem space, target audience, and business goals.
- Define: Clearly articulating user needs, pain points, and desired outcomes.
- Dream: Brainstorming innovative solutions and exploring various design possibilities.
- Design: Creating wireframes, prototypes, and visual designs that align with user needs and business goals.
- Develop: Building the application, ensuring it meets quality standards and technical requirements.
- Deploy: Launching the application and making it available to users.
- Diagnose: Gathering user feedback, analyzing usage data, and identifying areas for improvement.
The 7D Product Design Process
1. Discover
The Discover phase is all about understanding the context in which the application will exist. It involves conducting user research, analyzing market trends, and identifying business goals. Key activities in this phase include:
- User Research: Conducting surveys, interviews, and usability testing to understand user needs, behaviors, and motivations.
- Market Analysis: Identifying competitors, analyzing their strengths and weaknesses, and understanding market trends.
- Business Goals: Defining the objectives of the application and how it will contribute to the overall business strategy.
2. Define
In the Define phase, the insights gathered during the Discover phase are synthesized to create a clear definition of the problem and the desired solution. Key activities in this phase include:
- User Personas: Creating representative archetypes of target users to guide design decisions.
- User Stories: Developing narratives that describe how users will interact with the application and what they hope to achieve.
- Problem Statement: Clearly articulating the problem that the application aims to solve.
3. Dream
The Dream phase is where creativity and innovation take center stage. The goal is to generate a wide range of ideas and explore different design possibilities. Key activities in this phase include:
- Brainstorming: Generating a large number of ideas, encouraging out-of-the-box thinking.
- Sketching: Quickly visualizing ideas on paper to explore different design directions.
- Storyboarding: Creating visual narratives to illustrate how users will interact with the application.
4. Design
In the Design phase, the focus shifts from ideation to creating concrete designs. This involves developing wireframes, prototypes, and visual designs that align with user needs and business goals. Key activities in this phase include:
- Wireframing: Creating low-fidelity representations of the application’s layout and functionality.
- Prototyping: Developing interactive mockups to simulate the user experience.
- Visual Design: Creating the visual style and branding of the application.
5. Develop
The Develop phase is where the application is built, tested, and refined. This involves collaboration between designers, developers, and testers to ensure the application meets quality standards and technical requirements. Key activities in this phase include:
- Coding: Writing the code that powers the application.
- Testing: Conducting various tests to identify and fix bugs.
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring the application meets quality standards and user expectations.
6. Deploy
The Deploy phase involves launching the application and making it available to users. This includes preparing the application for release, deploying it to the appropriate platforms, and communicating with users. Key activities in this phase include:
- Release Planning: Defining the release timeline and coordinating with stakeholders.
- Deployment: Making the application available to users through app stores or other channels.
- Marketing & Communication: Promoting the application and informing users about its features and benefits.
7. Diagnose
The Diagnose phase is crucial for continuous improvement. It involves gathering user feedback, analyzing usage data, and identifying areas for improvement. Key activities in this phase include:
- User Feedback: Collecting feedback from users through surveys, reviews, and social media.
- Usage Analytics: Tracking how users interact with the application to identify patterns and areas for improvement.
- Iteration & Refinement: Using the insights gathered to make necessary updates and improvements to the application.
Benefits of 7D Product Design
- User-Centered Approach: 7D Product Design puts the user at the heart of the process, ensuring the application meets their needs and expectations.
- Collaboration & Communication: The framework fosters collaboration and communication among designers, developers, and stakeholders.
- Iterative Development: The iterative nature of the process allows for continuous improvement and adaptation to user feedback.
- Comprehensive Coverage: 7D Product Design covers all aspects of the application development lifecycle, from ideation to post-launch analysis.
Conclusion
7D Product Design offers a holistic and human-focused approach to application development. By emphasizing user needs, collaboration, and iterative development, it empowers teams to create successful applications that delight users and achieve business goals.