Design is an intricate and multifaceted discipline that requires a structured approach to ensure success.
Whether you’re designing a user interface, a product, or a service, following a well-defined design process can help you create solutions that are both effective and user-friendly.
In this post, we’ll explore the design process in detail, drawing on the insights from the Wuppertal Design Process Chart and other industry best practices.
Introduction to the Design Process
The design process is a series of steps that designers follow to create a product or service. It involves understanding the problem, generating ideas, refining those ideas, and finally implementing the solution.
The process is iterative, meaning that designers often go back and forth between steps to refine their work.
Why is the Design Process Important?
A structured design process helps designers:
- Stay organized and focused
- Ensure that all aspects of the problem are considered
- Collaborate effectively with team members
- Create solutions that meet user needs
- Reduce the risk of costly mistakes
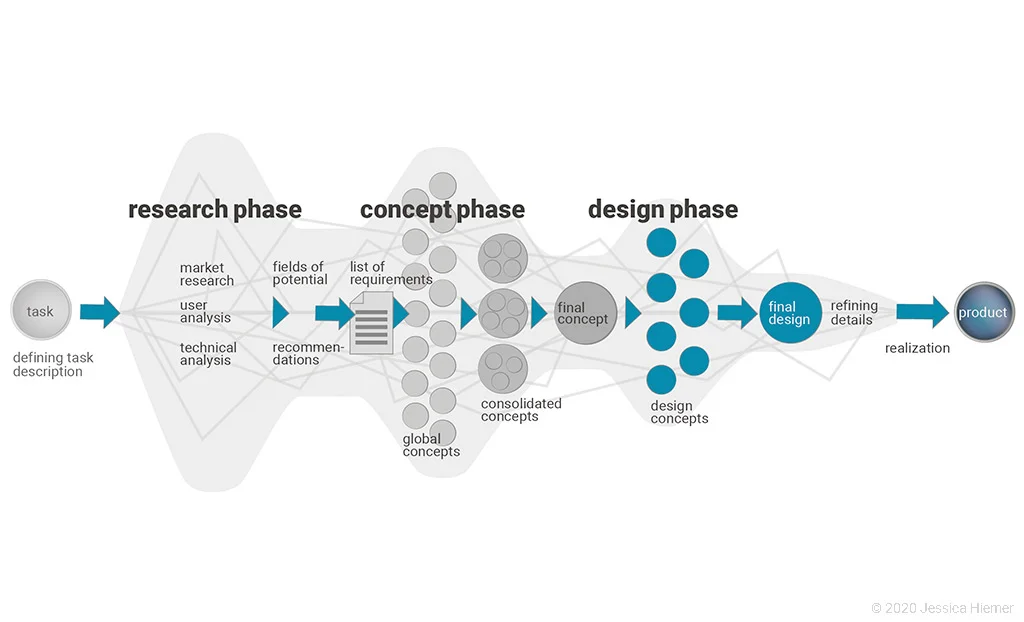
The Wuppertal Design Process Chart
The Wuppertal Design Process Chart, as shared in the image, outlines a clear and structured approach to design. Let’s break down each phase of the process:
1. Research Phase
The research phase is the foundation of the design process. It involves gathering information about the market, users, and technical requirements.
Market Research
Market research helps designers understand the competitive landscape. It involves analyzing competitors, identifying market trends, and understanding the needs and preferences of the target audience. Tools like Google Trends and Statista can provide valuable insights.
User Analysis
User analysis focuses on understanding the needs, behaviors, and pain points of the end-users. Techniques such as user interviews, surveys, and usability testing are commonly used. Websites like Nielsen Norman Group offer extensive resources on user research methods.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis involves understanding the technical constraints and opportunities of the project. This includes evaluating the available technologies, platforms, and tools that will be used to implement the design.
2. Fields of Potential
Once the research is complete, the next step is to identify fields of potential. This involves brainstorming and exploring different ideas and concepts that could address the problem. Techniques like mind mapping and SWOT analysis can be useful in this phase.
3. Recommendations
Based on the research and brainstorming, designers can make recommendations for the best course of action. This involves prioritizing ideas and concepts that have the most potential for success.
4. List of Requirements
Creating a list of requirements is crucial for ensuring that the final design meets all the necessary criteria. This list should include functional requirements, user needs, technical constraints, and any other relevant factors.
5. Consolidated Concepts
In this phase, designers consolidate the best ideas into coherent concepts. This involves creating sketches, wireframes, and prototypes to visualize the concepts. Tools like Figma and Adobe XD are commonly used for this purpose.
6. Global Concepts
Global concepts involve refining the consolidated concepts to ensure they are scalable and applicable across different markets and user groups. This is particularly important for products that will be used internationally.
7. Design Phase
The design phase is where the concepts are turned into tangible designs. This phase involves several steps:
Final Concept
The final concept is the refined version of the best idea. It should be well-defined and ready for detailed design work.
Final Design
The final design involves creating high-fidelity mockups and prototypes. This is where the visual design, interaction design, and user experience come together.
Refining Details
Refining details involves making small adjustments to improve the design. This could include tweaking the layout, adjusting colors, or improving the user interface.
Production
The production phase involves preparing the design for implementation. This includes creating design specifications, assets, and documentation for developers.
Realization
Realization is the final step in the design process, where the design is implemented and brought to life. This could involve coding, manufacturing, or other forms of production.
8. Task
The task phase involves defining the specific tasks that need to be completed to achieve the design goals. This includes creating a task description, setting deadlines, and assigning responsibilities.
Best Practices for the Design Process
To ensure a successful design process, consider the following best practices:
1. Collaborate with Stakeholders
Involve stakeholders throughout the design process to ensure that their needs and expectations are met. Regular communication and feedback sessions are essential.
2. Iterate and Test
Design is an iterative process. Continuously test your designs with real users and make improvements based on their feedback. Usability testing tools like UserTesting can be invaluable.
3. Stay User-Centered
Always keep the end-user in mind. Use personas and user journeys to guide your design decisions and ensure that the final product meets user needs.
4. Document Everything
Document each step of the design process, including research findings, design decisions, and feedback. This helps maintain clarity and provides a reference for future projects.
5. Use the Right Tools
Leverage design tools that streamline the process and improve collaboration. Popular tools include Sketch, InVision, and Axure.
Conclusion
The process is a critical component of creating successful products and services. By following a structured approach like the one outlined in the Wuppertal Design Process Chart, designers can ensure that their work is thorough, user-centered, and effective. Remember to stay flexible and adapt the process to fit the specific needs of your project.
For more insights and resources on the design process, check out the following links:
By following these guidelines and utilizing the right tools, you can master the design process and create exceptional user experiences.
The image used in this post belongs to Jessica Hiemer