User Experience (UX) design process is at the heart of crafting digital products that users love.
It’s more than just creating visually appealing interfaces; it’s about understanding user needs and delivering seamless, meaningful interactions.
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, an effective UX design process is not a luxury but a necessity. Did you know that 88% of users won’t return to a website after a poor experience? That’s a compelling reason to get UX right.
This post dives deep into the 8 steps of the UX design process, enriched by over two decades of industry experience. We’ll break down each stage, its importance, and actionable insights to guide you through building exceptional user experiences. Whether you’re a seasoned designer or new to UX, this guide is designed to inspire and inform.
What Is the UX Design Process?
At its core, the UX design process involves creating products that are:
- Usable: Easy for users to navigate and complete tasks.
- Accessible: Inclusive of diverse user needs and abilities.
- Functional: Meeting technical requirements without compromising experience.
- Engaging: Reflecting the brand’s identity and fostering connection.
- Satisfying: Leaving users delighted with their interactions.
While every project has its nuances, the core principles of UX design remain consistent. They revolve around research, testing, and iteration—all aimed at creating user-centered designs.
Why Is UX Design Critical?
UX design isn’t just a box to check off; it’s a game-changer for businesses. Consider these statistics:
- 70% of online businesses fail due to bad usability (WebFX).
- A well-designed user interface can raise your website’s conversion rate by 200% to 400% (Forrester).
- Companies that invest in UX see an average return of $100 for every $1 spent (UX Design Institute).
Industries such as healthcare, real estate, and fintech heavily rely on UX to differentiate themselves in competitive markets. By prioritizing user experience, businesses can improve customer retention, boost sales, and build lasting brand loyalty.
Core UX Concepts
Before diving into the process, it’s essential to understand foundational UX methodologies:
- Design Thinking: A human-centered approach involving Empathy, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test.
- Agile UX: Integrating UX design into Agile development cycles to deliver iterative improvements.
- Lean UX: Focusing on collaboration and rapid experimentation over heavy documentation.
These methodologies set the stage for a well-structured UX process that adapts to project requirements.
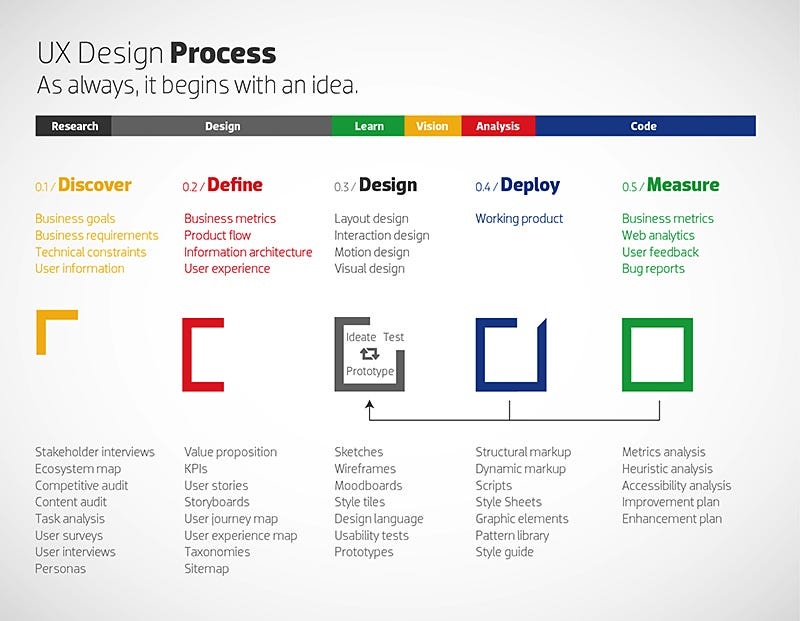
The Steps of the UX Design Process
1. Stakeholder Interviews: Setting the Foundation
Before crafting solutions, understand the problem. Stakeholder interviews clarify business goals, challenges, and project expectations. Questions to ask include:
- What are the primary objectives of this product?
- Who is the target audience?
- What are the key performance indicators (KPIs)?
By aligning with stakeholders, designers ensure that their work supports broader business objectives.
2. User Research: Empathizing with Your Audience
Empathy is the cornerstone of UX. Research methods like surveys, user interviews, and usability testing reveal user needs, pain points, and behaviors. Key techniques include:
- Contextual Inquiries: Observing users in their environment.
- Competitor Analysis: Learning from similar products.
- Data Analytics: Understanding user behavior patterns.
The goal is to create a user-first perspective that informs every design decision.
3. User Personas and User Flows: Understanding User Journeys
Personas are fictional but research-driven representations of your target audience. They answer questions like:
- Who are the users?
- What are their goals and motivations?
Meanwhile, user flows map the steps users take to achieve those goals, providing a blueprint for intuitive navigation.
4. Information Architecture: Organizing Content Effectively
Information architecture (IA) ensures that users can easily find what they need. Tools like sitemaps and card sorting help organize content logically. A well-structured IA:
- Reduces user frustration.
- Improves task completion rates.
- Enhances overall usability.
5. Wireframes: Designing the Blueprint
Wireframes are skeletal designs that focus on structure and functionality rather than aesthetics. They help teams:
- Visualize page layouts.
- Plan interactions.
- Align on functionality early.
Popular tools include Figma, Sketch, and Adobe XD.
6. Interactive Prototypes: Bringing Ideas to Life
Prototypes transform static wireframes into clickable, interactive mockups. This step bridges the gap between concept and reality, allowing stakeholders to:
- Experience the design firsthand.
- Identify potential usability issues.
- Provide actionable feedback.
7. Prototype Testing: Validating Designs
Testing prototypes with real users ensures that designs meet their needs. Methods include:
- A/B Testing: Comparing two design variations.
- Usability Testing: Observing users as they interact with the prototype.
- Feedback Sessions: Gathering qualitative insights from users.
The insights gained drive iterative improvements.
8. Iteration: Refining the Design
UX design is never truly “done.” Iteration is an ongoing process where designers:
- Implement feedback.
- Address usability concerns.
- Adapt to changing user needs or market trends.
Best Practices for Successful UX Design
To excel in UX design, follow these best practices:
- User-Centered Focus: Involve users at every stage of the process.
- Collaboration: Work closely with developers, marketers, and stakeholders.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Use analytics and feedback to guide improvements.
- Design Sprints: Solve critical challenges in a structured, time-bound manner.
- Continuous Learning: Stay updated with the latest tools and trends.
Tools of the Trade
Modern UX design relies on an array of tools for research, design, and testing:
- Research: Google Analytics, Hotjar, and Typeform.
- Design: Figma, Adobe XD, and Sketch.
- Prototyping: InVision, Axure, and ProtoPie.
- Collaboration: Miro, Slack, and Jira.
These tools streamline workflows and enhance collaboration across teams.
Conclusion
The UX design process is both an art and a science. By following these steps, you’ll create products that resonate with users and achieve business goals. Whether you’re designing a simple app or a complex enterprise platform, remember: the user always comes first.
Are you ready to elevate your UX game? Start applying these principles today, and watch your designs transform into user favorites.