User research isn’t a luxury—it’s the oxygen of human-centered design. Get it wrong, and you’ll build solutions that miss the mark. Get it right, and you unlock products users love. But with so many methods floating around, how do you navigate the chaos? Let’s break down the four core types of UX research, their goals, real-world applications, and the battle-tested frameworks that separate pros from amateurs.
The Five Non-Negotiable Steps of UX Research
Before diving into research types, master this universal process:
Define Objectives: What problem are you solving? (e.g., “Why do users abandon checkout?”)
Choose Methods: Match methods to questions (more on this below).
Recruit Participants: Aim for representative users—not colleagues! (Tools: User Interviews, Respondent).
Conduct & Document: Record sessions (Tools: Otter.ai for transcripts, Dovetail for analysis).
Synthesize & Act: Turn data into decisions (Frameworks: Affinity Mapping, Jobs To Be Done).
⚡️ Pro Tip: Double your impact by involving stakeholders in Step 5. Seeing raw user pain points builds empathy fast.
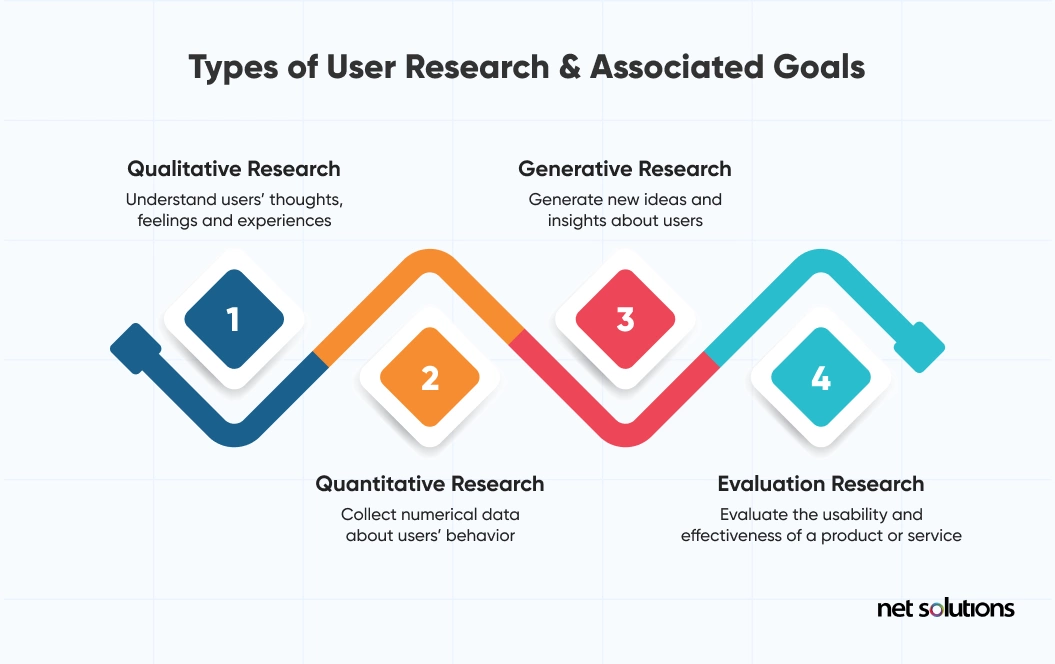
1. Qualitative Research: The “Why” Behind Behavior
Goal: Uncover users’ thoughts, feelings, and unspoken motivations.
When to Use: Early discovery phases or when exploring complex behaviors.
Methods & Tools:
User Interviews (1:1 deep dives):
Framework: The “5 Whys” to drill into root causes.
Tool: Lookback for live note-taking.
Focus Groups (Group dynamics exploration):
Caution: Groupthink distorts truth! Use for idea generation, not behavioral insights.
Diary Studies (Longitudinal context):
Tool: dscout for capturing in-the-moment experiences.
Case Study: Spotify’s “Day in the Life” diaries revealed users skipped podcasts during commutes due to data limits. Result: Offline listening mode.
🔍 Deep Dive: Qualitative data thrives on small samples (5–10 users). Focus on richness, not representativeness.
2. Generative Research: Fueling Innovation
Goal: Generate ideas and uncover unmet needs.
When to Use: Before a product exists—or when reinventing a category.
Methods & Tools:
Card Sorting (IA foundation):
Framework: Open vs. Closed sorting (Optimal Workshop).
Pro Insight: Run remotely to avoid influencing participants.
Brainstorming Sessions (Stakeholder + user co-creation):
Framework: Design Sprints (Google Ventures).
Ethnographic Field Studies (Contextual observation):
Tool: Notion for pattern tracking.
Case Study: Airbnb’s live “host-renter” workshops generated 12 ideas for trust-building features in 2 days.
💡 UX Truth: Generative research fails without diverse voices. Include edge-case users!
3. Quantitative Research: The “What” and “How Much”
Goal: Measure behavior at scale.
When to Use: Validating hypotheses or tracking UX metrics pre/post-launch.
Methods & Tools:
Surveys (Broad sentiment capture):
Framework: System Usability Scale (SUS) for standardized scoring.
Tool: Typeform for engaging designs.
A/B Testing (Performance showdown):
Framework: Statistical significance calculators (Optimizely Stats Engine).
Pitfall: Never test more than 2 variables concurrently!
Eye-Tracking (Visual attention mapping):
Case Study: Duolingo’s A/B test revealed gamified streaks increased daily usage by 22%.
📊 Data Trap: Quantitative alone is shallow. Pair it with qual to understand why metrics shift.
4. Evaluative Research: Stress-Testing Your Product
Goal: Test usability and effectiveness.
When to Use: During prototyping or post-launch optimization.
Methods & Tools:
Usability Testing (Task-based validation):
Framework: Think-Aloud Protocol (Nielsen Norman).
Tool: UserTesting.com for rapid feedback.
Heuristic Evaluation (Expert audit):
Framework: Nielsen’s 10 Heuristics (downloadable checklist).
Accessibility Audits (Inclusion compliance):
Tool: axe DevTools for WCAG checks.
Case Study: After evaluative testing, GOV.UK simplified form fields, reducing errors by 62% (source).
🚨 Red Flag: If users struggle with your prototype, never blame them. Restructure the task.
Choosing Your Method: A Decision Tree
Use this cheat sheet to match methods to goals:
| Research Goal | Best Methods |
| Understand emotions | Interviews, Diary Studies |
| Discover new ideas | Card Sorting, Field Studies |
| Measure behavior | Surveys, A/B Tests |
| Test usability | Usability Testing, Heuristics |
Mixed-Methods Magic: Combine qual + quant (e.g., follow up a survey with interviews to explore outlier responses).
The Future: Emerging Trends
Biometric Tools: Pupil Labs for emotion tracking.
AI Synthesis: Revelo auto-themes 100+ interviews in minutes.
Remote Research: Post-COVID, hybrid models dominate (Ethnio for recruitment).
Key Takeaways
Qualitative = Depth, Quantitative = Breadth.
Generative sparks ideas; Evaluative refines execution.
Always start with goals—never let tools drive the process.
Ethics are non-negotiable: Obtain consent, anonymize data, and compensate participants.
🌟 Final Wisdom: Research isn’t a phase—it’s a cycle. Revisit it at every major product milestone.
Further Reading: